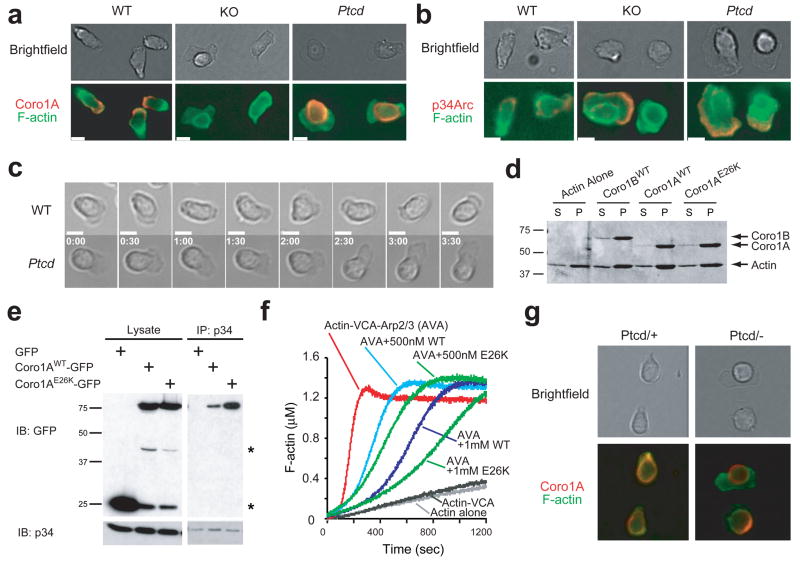
Figure 6. E26K mutation alters Coro1A cellular distribution and regulation of Arp2/3. (a–c).
Immunofluorescent microscopy of T cells migrating on ICAM-coated coverslips in 1 ug/mL CCL21. Cells were stained for F-actin and (a) Coro1A or (b) Arp2/3 subunit p34 (b); and still images from brightfield time-lapse microscopy (c). White bar indicates 5 microns. Time stamp reflects min:sec. Data are representative of three experiments. (d) Co-sedimentation assay of indicated purified coronins and F-actin. S, supernatent. P, pellet. (e) Lysates from HEK293FT cells expressing indicated constructs were immunoprecipitated with anti-p34 and blotted with indicated antibodies. *GFP degradation bands. (f) Arp2/3-induced actin polymerization assay with indicated concentrations of purified coronins. WT, wild-type coronin. E26K, mutant coronin. AVA, standard mixture of actin, VCA and Arp2/3 complex (g) T cells from Ptcd/+ and Ptcd/− stained as in a.