Abstract
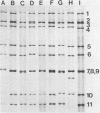
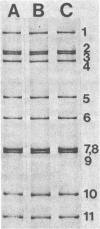
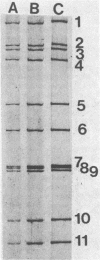
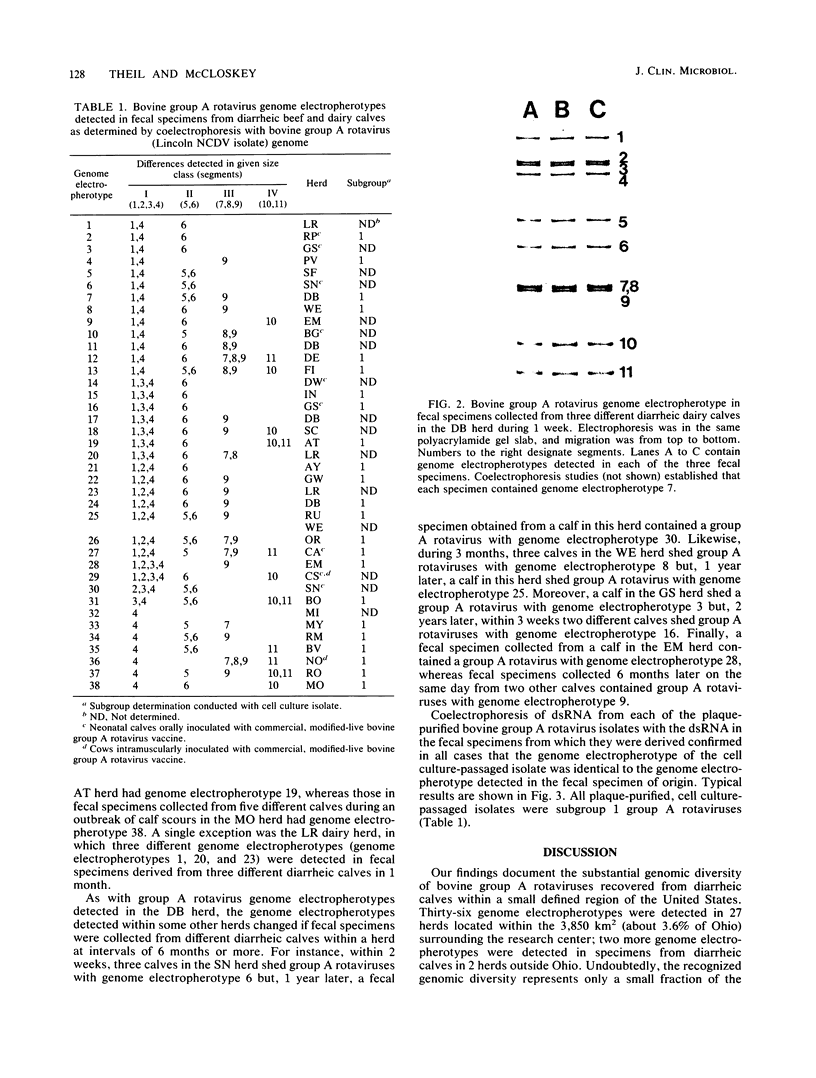
The genome electropherotyping technique was used to examine group A rotaviral infections of diarrheic calves ranging from 1 to 85 days of age in 2 beef and 27 dairy herds. Coelectrophoresis studies demonstrated 38 distinct bovine group A rotavirus genome electropherotypes; all were long genome electropherotypes, and none had extra segments or unusual segment rearrangements. Genome electropherotypes in fecal specimens from diarrheic calves previously inoculated orally with a commercial, modified-live group A rotavirus vaccine differed from the vaccine genome electropherotype. Generally, when fecal specimens for genome electropherotyping were collected from two or more different calves within the same herd over a relatively short time, only one genome electropherotype was detected within a given herd. Different genome electropherotypes were detected in the same herd, however, when fecal specimens were obtained from different diarrheic calves over longer intervals (6 months or more). Twenty-three group A rotavirus strains with distinct genome electropherotypes, from diarrheic calves in 22 herds, were isolated and plaque purified in cell culture, and all were subgroup 1 group A rotaviruses. Non-group A rotavirus genome electropherotypes were not detected in 131 fecal specimens, negative for group A rotavirus, collected from diarrheic calves in 17 dairy herds.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Bishop R. F., Shann F. A. Epidemiology of rotavirus diarrhea in the Highlands of Papua, New Guinea, in 1979, as revealed by electrophoresis of genome RNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):162–164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.162-164.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert M. J., Soenarto Y., Bishop R. F. Epidemiology of rotavirus diarrhea in Yogyakarta, Indonesia, as revealed by electrophoresis of genome RNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):731–733. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.731-733.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinzoni R. C., Mattion N., La Torre J. L., Scodeller E. A. Incidence of rotavirus in beef herds in Argentina. Res Vet Sci. 1987 Mar;42(2):257–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash P., Freebain E., Brown T., Reid T. M. Molecular epidemiology of human rotavirus. J Hyg (Lond) 1986 Apr;96(2):265–275. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400066043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Avendaño L. F., Muñoz O., Romero P., Eternod J. G., Lopez S., Moncaya J. Comparison of human rotaviruses isolated in Mexico City and in Santiago, Chile, by electrophoretic migration of their double-stranded ribonucleic acid genome segments. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):342–348. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.342-348.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Calderón E., González N., Salomon A., Martuscelli A., Romero P. Presence of two distinct types of rotavirus in infants and young children hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Mexico City, 1977. J Infect Dis. 1979 Apr;139(4):474–477. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijtman N. L., Barrandeguy M. E., Cornaglia E. M., Schudel A. A. Variations and persistency of electropherotypes of bovine rotavirus field isolates. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;96(3-4):275–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01320968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Desselberger U. Cocirculation of different rotavirus strains in a local outbreak of infantile gastroenteritis: monitoring by rapid and sensitive nucleic acid analysis. J Med Virol. 1983;11(1):39–52. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890110106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Sato T., Suzuki H., Kitaoka S., Katsushima N., Sakamoto M., Yazaki N., Ishida N. Changing RNA patterns in rotaviruses of human origin: demonstration of a single dominant pattern at the start of an epidemic and various patterns thereafter. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):683–687. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Kono M., Underdahl N. R., Twiehaus M. J. Cell culture propagation of neonatal calf diarrhea (scours) virus. Can Vet J. 1971 Mar;12(3):69–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J. Evidence for serotypic variation among bovine rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1984;79(3-4):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01310809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock D. H. Characterisation of rotavirus isolates from sub-clinically infected calves by genome profile analysis. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Jan;13(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock D. H. Isolation and characterization of two group A rotaviruses with unusual genome profiles. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):653–660. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Birch C., McLean B., Holmes I. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotaviruses in Melbourne, Australia, from 1973 to 1979, as determined by electrophoresis of genome ribonucleic acid. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):272–278. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.272-278.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabara M., Deregt D., Babiuk L. A., Misra V. Genetic heterogeneity within individual bovine rotavirus isolates. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):813–822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.813-822.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Variation in human rotavirus electropherotypes occurring between rotavirus gastroenteritis epidemics in central Australia. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):17–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.17-21.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J., Campbell I., Inglis J. M., Hargreaves F. D. Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):909–914. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer E., Avendaño F., Araya M. Characteristics and analysis of electropherotypes of human rotavirus isolated in Chile. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jul;148(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele A. D., Alexander J. J. Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus in black infants in South Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2384–2387. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2384-2387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M. Partial characterization of a bovine group A rotavirus with a short genome electropherotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1094–1099. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1094-1099.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Moorhead P. D., Whitmoyer R. E. Porcine rotavirus-like virus (group B rotavirus): characterization and pathogenicity for gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.340-345.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly E., Cohen J. Demonstration of size variation of RNA segments between different isolates of calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):583–586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderfecht S. L., Eiden J. J., Torres A., Miskuff R. L., Mebus C. A., Yolken R. H. Identification of a bovine enteric syncytial virus as a nongroup A rotavirus. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1913–1918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]