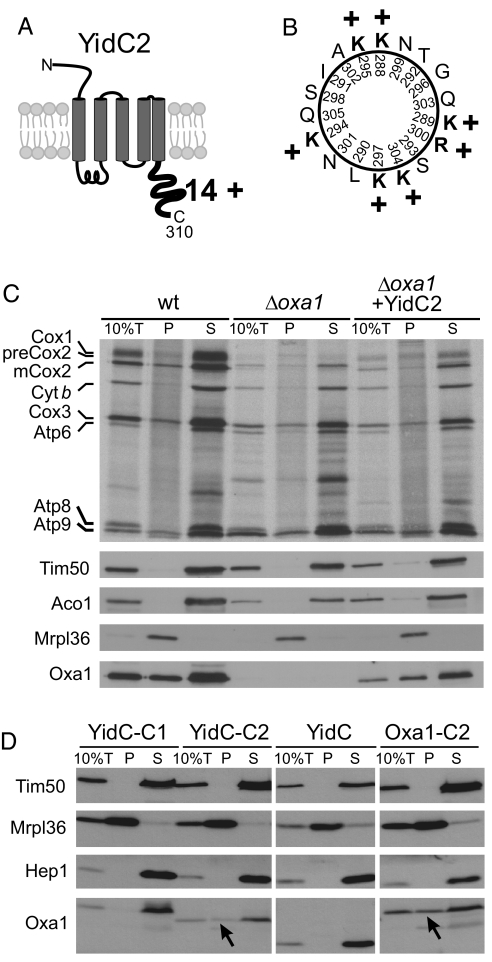
Fig. 4.
YidC2 binds to mitochondrial ribosomes. (A) Schematic representation of the predicted topology and the cytoplasmic extension of S. mutans YidC2. The C-terminal tail domain is very basic and has a net charge of + 14 as indicated. (B) Helical-wheel representation of YidC2 C-terminal residues 288–305. Positively charged residues are shown in bold. (C) Translation products were radiolabeled for 15 min at 25 °C in isolated mitochondria of the indicated strains. Ten percent of the sample total (10%T) was directly applied to the gel. The residual extract was lysed in the high salt buffer and loaded on a layer of 1.2-M sucrose and centrifuged for 60 min at 190,000 × g. Proteins of the ribosome-containing pellet (P) and the supernatant (S) were analyzed by autoradiography and Western blotting. Oxa1 and YidC2 were detected with Oxa1-specific antibodies that recognize the N-terminal region that is shared by both proteins. Signals of the ribosomal protein Mrpl36, and of the non-ribosomal proteins Tim50, Hep1, and Aco1 are shown for control. Please note that the “smeary” background in the pellet lanes of the autoradiography is because of the presence of nascent chains that are associated with the translation-active ribosomes. Cyt b, cytochrome b. (D) Mitochondria were isolated from Δoxa1 strains expressing the fusion proteins indicated. The samples were fractionated as described in (C). Arrowheads indicate fusion proteins that comigrate with the ribosomal pellet.