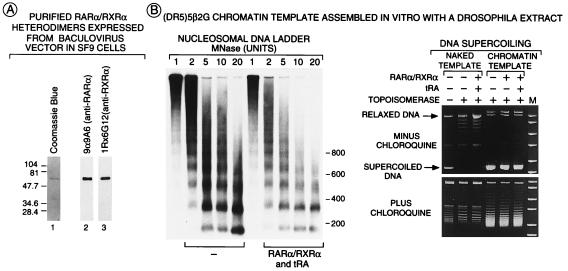
Figure 2.
Analysis of RARα/RXRα heterodimers and chromatin structure. (A) Purification of RARα/RXRα heterodimers. FhRARα and HmRXRα were coexpressed in Sf9 cells and were affinity-purified by using a Ni2+ column followed by anti-Flag agarose column that bind the HmRXR moiety and the FhRAR moiety of the heterodimer, respectively. Purified heterodimers (100 ng of protein) were separated on a 10% SDSPAGE gel before staining with Coomassie blue (lane 1) or Western blot analysis using mAbs recognizing either human RARα (lane 2) or mouse RXRα (lane 3). (B) Overall chromatin structure was not affected by RARα/RXRα heterodimers. Chromatin or naked (DR5)5β2G templates (200 pM) incubated in the presence or absence of FhRARα/HmRXRα (1 nM) and tRA (10−6 M) were digested with varying concentrations of micrococcal nuclease in a final volume of 80 μl, were separated on a 1.5% agarose gel, and were Southern blotted by using a [32P] probe corresponding to the −40 to +5 region of the (DR5)5β2G promoter. DNA supercoiling was estimated as described (35) on DNA (200 ng) treated (or not treated) by topoisomerase I (10 units; final volume of 45 μl). DNA was separated on a 1% agarose gel in the presence or absence of 1.2 μM chloroquine. Migration of relaxed and supercoiled template DNA is indicated.