Abstract
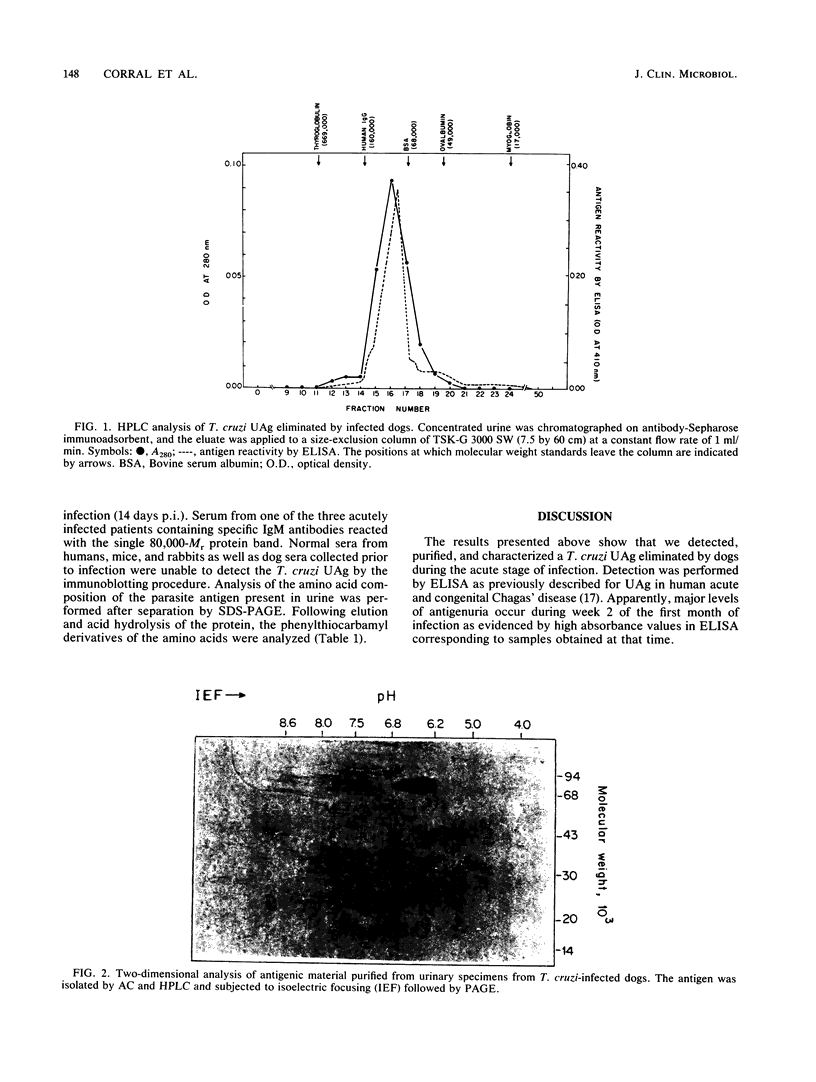
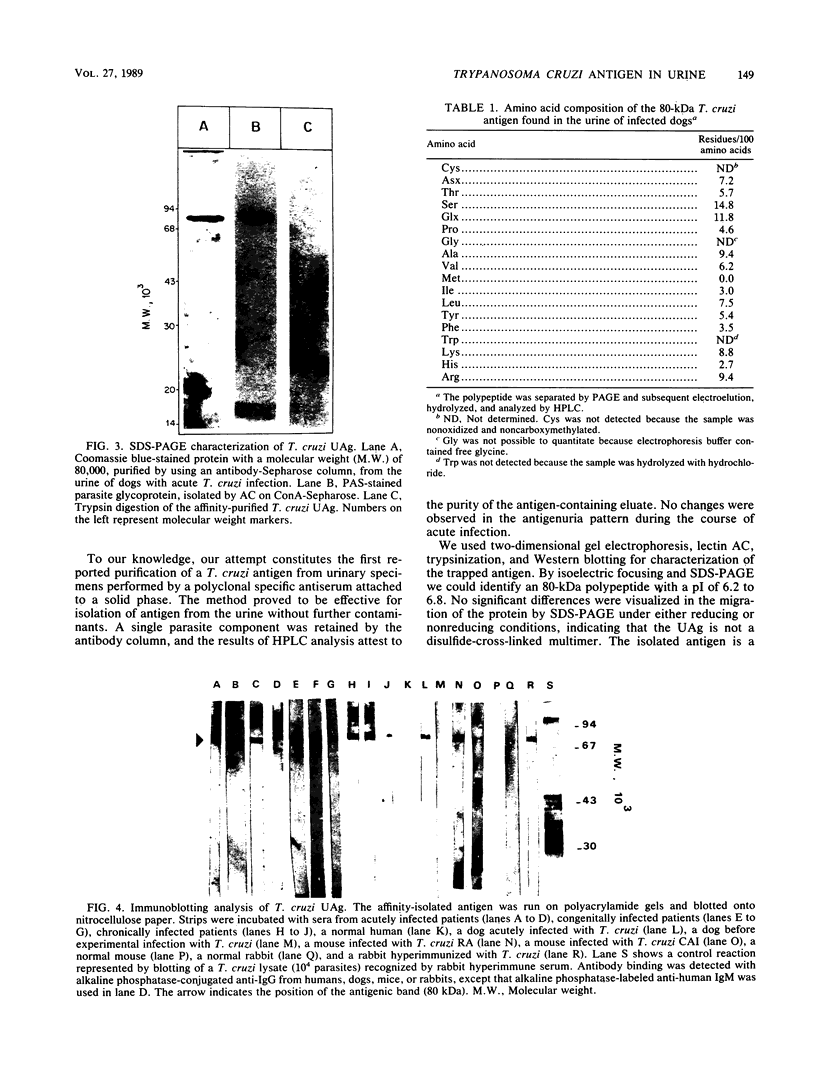
A Trypanosoma cruzi antigen eliminated in the urine of experimentally infected dogs was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay between 9 and 28 days after infection. The parasite urinary antigen (UAg) was purified by affinity chromatography with polyclonal antibodies to T. cruzi. The eluate of the antibody column was subjected to high-performance liquid chromatography and showed a single peak of A280. This antigen was the only parasite component found in the urine of infected dogs during the course of acute T. cruzi infection. Antigen characterization was performed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, lectin affinity chromatography, proteolytic digestion, and Western blotting (immunoblotting). The isolated UAg exhibited a relative molecular size of 80 kilodaltons (kDa), an isoelectric point of 6.2 to 6.8, binding to concanavalin A, and sensitivity to trypsin. The parasite antigen was electroeluted from polyacrylamide gels and subjected to acid hydrolysis and amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. The 80-kDa glycoprotein was recognized by serum antibodies from a wide variety of T. cruzi-infected hosts. The UAg proved to be a highly antigenic component present in different strains of T. cruzi. This 80-kDa polypeptide resembles one of the parasite antigens previously found in the urine of patients with acute Chagas' disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. W., Katzin A. M., Colli W. Mapping of surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma cruzi by two-dimensional electrophoresis. A correlation with the cell invasion capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):599–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G., Chiari E., Dias J. C. Demonstration of Trypanosoma cruzi antigen in serum from patients with Chagas' disease. Lancet. 1981 Jan 31;1(8214):246–249. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo F. G. Detection of circulating antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi by enzyme immunoassay. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1982 Feb;76(1):25–36. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1982.11687501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard C. A., Wrightsman R. A., Manning J. E. Identification of monoclonal antibodies against the trypomastigote stage of Trypanosoma cruzi by use of iminobiotinylated surface polypeptides. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Aug;16(2):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongertz V., Hungerer K. D., Galvão-Castro B. Trypanosoma cruzi: circulating antigens. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1981 Jan-Mar;76(1):71–82. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02761981000100008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral R., Freilij H., Grinstein S. Specific circulating immune complexes in acute Chagas' disease. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1987 Jan-Feb;29(1):26–32. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651987000100004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lederkremer R. M., Alves M. J., Fonseca G. C., Colli W. A lipopeptidophosphoglycan from Trypanosoma cruzi (epimastigota). Isolation, purification and carbohydrate composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragon E. A., Brothers V. M., Wrightsman R. A., Manning J. A Mr 90 000 surface polypeptide of Trypanosoma cruzi as a candidate for a Chagas' disease diagnostic antigen. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Sep;16(3):213–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilij H., Muller L., Gonzalez Cappa S. M. Direct micromethod for diagnosis of acute and congenital Chagas' disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):327–330. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.327-330.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Snary D., Allen A. K. Comparative compositions of cell surface glycoconjugates isolated from Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 27;842(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freilij H. L., Corral R. S., Katzin A. M., Grinstein S. Antigenuria in infants with acute and congenital Chagas' disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):133–137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.133-137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González Cappa S. M., Bijovsky A. T., Freilij H., Muller L., Katzin A. M. Aislamiento de una cepa de trypanosoma cruzi a predominio de formas delgadas en la Argentina. Medicina (B Aires) 1981;41(1):119–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González Cappa S. M., Chiale P., del Prado G. E., Katzin A. M., de Martini G. W., de Isola E. D., Abramo Orrego L., Segura E. L. Aislamiento de uan cepa de Trypanosoma cruzi de un Paciente con miocardiopatía chagásica cronica y su caracterización biológica. Medicina (B Aires) 1980;40 (Suppl 1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. A carbohydrate-containing antigen from Trypanosoma cruzi and its detection in the circulation of infected mice. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):465–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J., Gobel R. J. Rapid optimization of immunoadsorbent characteristics. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):113–120. doi: 10.1042/bj2210113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzin A. M., Colli W. Lectin receptors in Trypanosoma cruzi. An N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-containing surface glycoprotein specific for the trypomastigote stage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 19;727(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Manning J. E. Major surface proteins and antigens on the different in vivo and in vitro forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:119–131. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller L. A., Añasco N., González Cappa S. M. Trypanosoma cruzi: isolate dependence in the induction of lytic antibodies in the mouse and rabbit. Exp Parasitol. 1986 Jun;61(3):284–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(86)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Chaplan S., Tydings J. D., Unkeless J., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi. Surface antigens of blood and culture forms. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Garcia Pons F., Eisen H. Antigenic polymorphism of Trypanosoma cruzi: clonal analysis of trypomastigote surface antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1984 May;14(5):392–399. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Cossio P. M., Arana R. M., Urman J., Kreutzer E., Laguens R. P., Segal A., Coarasa L. Immunologic and immunopathologic studies in congenital Chagas' disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Nov;4(4):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingales B., Andrews N. W., Kuwajima V. Y., Colli W. Cell surface antigens of Trypanosoma cruzi: possible correlation with the interiorization process in mammalian cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Aug;6(2):111–124. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Siqueira A. F., Filho F. F., Ribeiro R. D. Aspectos imunitários iniciais observados em ratos infectados por Trypanosoma cruzi. II. A circulaço de antígenos solúveis e as modificaçes do complemento sérico dos animais em dias sucessivos da infecço. Rev Bras Pesqui Med Biol. 1979 Apr;12(1):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]