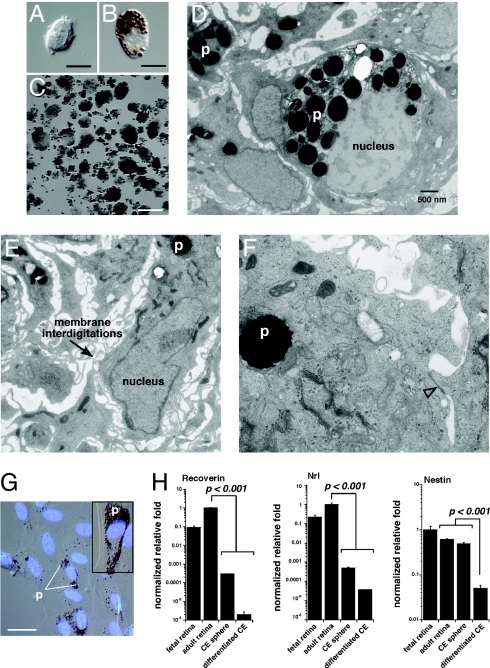
Fig. 7.
Human CE-derived spheres are made up of pigmented CE cells. (A and B) Postmortum human eyes were used as a source of CE cells for culture experiments. Dissociated human CE cell preparations were made up of pigmented and nonpigmented cells as for the mouse CE. (C) Clonogenic spheres from postmortum human CE samples. (D–F) TEM analysis of human CE-derived spheres showing pigment (p), membrane interdigitations, and epithelial junctions (open arrowhead). (G) Human CE-derived spheres were differentiated for 21 days coverslides as described for mouse CE-derived spheres. The cells spread out along the coverglass and took on the morphology of pigmented epithelial cells as for the mouse samples. (H) Real time RT-PCR analysis of human CE-differentiation cultures revealed that these cells did not express photoreceptor genes (recoverin, Nrl) or neural progenitor cell genes (nestin). Each bar represents the mean and standard deviation from duplicate experiments for at least 3 independent samples for each piece of tissue. Abbreviations: p, pigment. (Scale bars in A and B, 5 μm; C, 1 mm; G, 10 μm.)