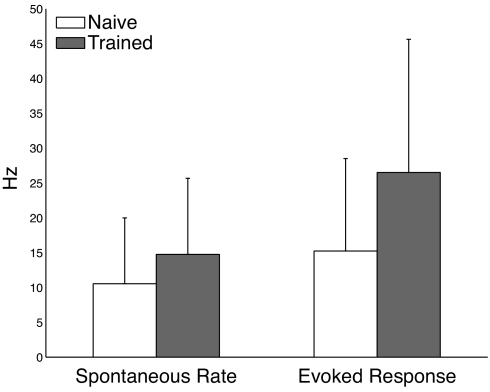
Fig. 5.
Experimental results demonstrating that training increases spontaneous firing rates and evoked responses as predicted by the model. Training evokes a 40% increase in the spontaneous firing rate and a 74% increase in evoked response. Error bars show standard deviation. Differences between naı̄ve and trained responses are statistically significant for both metrics (spontaneous P = 0.01, evoked P = 1.5 × 10−4).