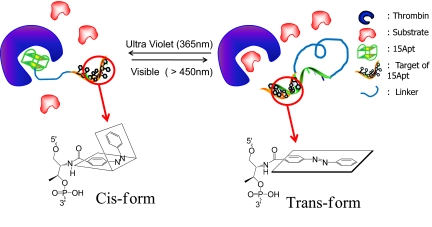
Fig. 1.
Xcomp/Yazo probes. The working principle is that dissociation and association of the 2 domains report high and quenched fluorescence signal, respectively. We assign test probes the following nomenclature. Xcomp equals the number of complementary sequences, and Yazo equals the number of incorporated azobenzene molecules. The trans- and cis- conformation is reversibly regulated by different input of electromagnetic radiation of the energy. Thus, when probes are treated with visible light, the regulatory domain is hybridized, and the probe is released from its target, resulting in activation of the enzyme (thrombin). When treated with UV light, probes form the open conformation, and the inhibitory domain can bind to the target, causing low enzymatic activity. The use of Xcomp/Yazo creates combinations that afford the opportunity to optimize probe design in accordance with thermal stability, thrombin affinity, and the results of clotting assays.