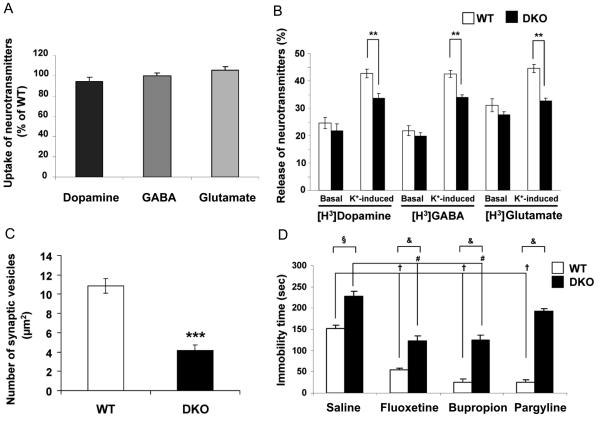
Fig. 6. Decreased secretion of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes of DKO mice.
(A) Uptake of [H3]dopamine, [H3]GABA and [H3]glutamate by synaptosomes of DKO mice as percentage of uptake by WT mice. Data are mean ± SEM from three separate experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Basal and K+-induced (25 mM) release of [H3]dopamine, [H3]GABA, and [H3]glutamate from synaptosomes of WT and DKO mice. The amount of radiolabelled neurotransmitter released, expressed as percentage of total radiolabelled neurotransmitter, is shown. Values are mean ± SEM from three separate experiments performed in triplicate; ** P<0.01. Open and closed bars represent WT and DKO mice, respectively. (C) Quantification of synaptic vesicles from 10 areas of hippocampus each representing 50 μm2. *** P<0.001. (D) Effect of neuropharmacologic agents on reducing the increased anxiety-like behavior in DKO mice (saline) as compared to WT mice, as measured by the decrease in immobility time in the tail suspenstion test (TST) (8-10 mice per group). (§) Untreated (saline) DKO mice differ significantly from untreated (saline) WT mice (P<0.001). (†) Treated (i.e., fluoxetine 20 mg/kg, bupropion 20 mg/kg, pargylene 75 mg/kg) WT mice differ significantly from untreated (saline) WT mice (P<0.001). (#) Fluoxetine and bupropion-treated DKO mice differ significantly from untreated (saline) DKO mice (P<0.001). (&) Treated DKO mice differ significantly from treated WT mice (P<0.001).