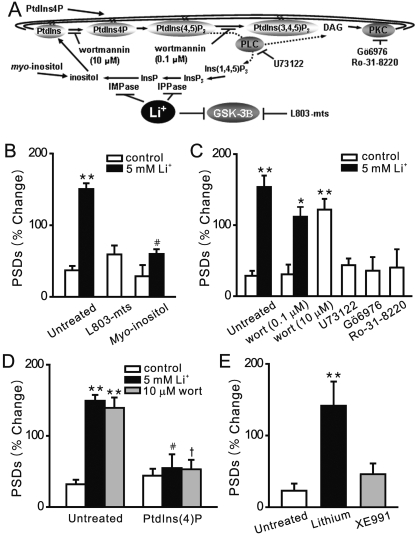
Fig. 5.
Inositol depletion mediates the effects of lithium on synapse formation. A,
the phosphoinositide cascade. B, bar graph summarizes the effects of
GSK-3β inhibitor L803-mts and exogenous myo-inositol on changes
in PSD95-GFP puncta (PSDs) after 4-h treatment under control (□) or
stimulated (5 mM Li+, ▪) conditions. Pretreatment with 1 mM
myo-inositol prevented the formation of new PSDs. C, bar graph
summarizes the effects of pharmacological modulation of the PtdIns cascade on
synapse formation in the absence (□) or presence of 5 mM lithium (▪).
Wortmannin [10 μM; wort (10 μM)] but not 100 nM wortmannin [wort(0.1
μM)] induced new synapse formation. Inhibition of PLC with 1 μM U73122
or inhibition of PKC with either 100 nM Gö6976 or 100 nM Ro-31-8220 did
not affect the number of PSD95-GFP puncta. D, bar graph summarizes the effects
on exogenous PtdIns(4)P on the number of PSD95-GFP puncta under control
conditions (□) and during treatment with 5 mM lithium (▪) or 10 μM
wortmannin ( ). PtdIns(4)P
was delivered via the shuttle PIP system as described under Materials and
Methods. E, bar graph summarizes the effects of 10 μM XE991 on the
number of PSD95-GFP puncta under control conditions
(
). PtdIns(4)P
was delivered via the shuttle PIP system as described under Materials and
Methods. E, bar graph summarizes the effects of 10 μM XE991 on the
number of PSD95-GFP puncta under control conditions
( ). Data are mean ±
S.E.M. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01
relative to untreated control; #, p < 0.01 relative to
lithium-induced response in the absence of other treatments (untreated);
†, p < 0.01 relative to wortmannin-induced response in the
absence of other treatments (untreated); ANOVA with Bonferroni post test.
). Data are mean ±
S.E.M. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01
relative to untreated control; #, p < 0.01 relative to
lithium-induced response in the absence of other treatments (untreated);
†, p < 0.01 relative to wortmannin-induced response in the
absence of other treatments (untreated); ANOVA with Bonferroni post test.