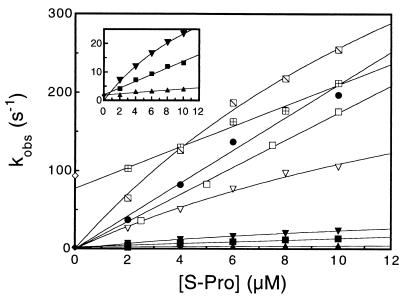
Figure 2.
Concentration dependence of the kinetics for S-peptide analogues binding to S-protein and the concentration-independent value of the dissociation rate constant for selected variants. All experiments were conducted under conditions described in Fig. 1a. Association kinetics were measured under pseudo-first-order conditions ([S-protein] = 5 × [S-peptide analogue]), and dissociation kinetics were measured in the presence of a 50- to 500-fold excess over RNaseS* of (unlabeled) Pep-1. Data for the slower-reacting variants are expanded in the inset. The concentration of the analogue is 0.4 μM, except for Pep-1F and H12A/M13MS⩵O, for which it is 0.2 μM. ●, Pep-1F; □, M13A;  , H12A; ⊞, H12A/M13MS⩵O; ■, F8A; ▿, A6G; ▾, A6P; ▴, Q11P. The symbols ⧫ and ◊ plotted at [S-protein] = 0 indicate the dissociation rate constants for H12A/M13MS⩵O and F8A, respectively, where the labeled analogues are competed-off RNaseS* by excess (unlabeled) Pep-1 (Fig. 1b). The data are fitted with a straight line or the Michaelis-Menten model (see text).
, H12A; ⊞, H12A/M13MS⩵O; ■, F8A; ▿, A6G; ▾, A6P; ▴, Q11P. The symbols ⧫ and ◊ plotted at [S-protein] = 0 indicate the dissociation rate constants for H12A/M13MS⩵O and F8A, respectively, where the labeled analogues are competed-off RNaseS* by excess (unlabeled) Pep-1 (Fig. 1b). The data are fitted with a straight line or the Michaelis-Menten model (see text).