Figure 2.
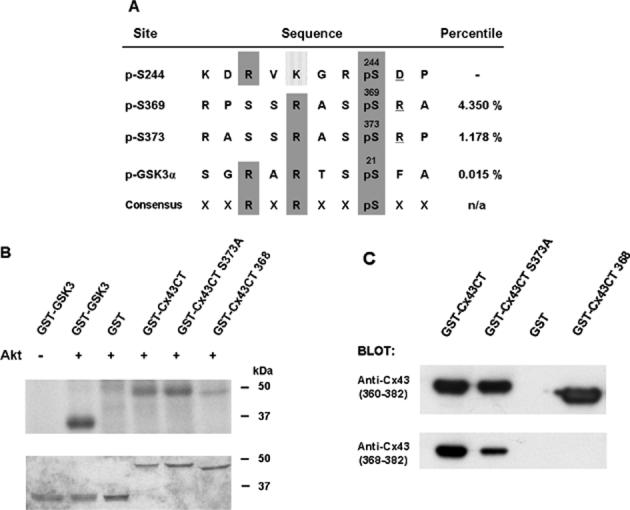
Cx43 is a substrate for Akt in vitro. (a) The alignment of potential Akt phosphorylation sites in Cx43 with a known Akt site in GSK3 and the consensus sequence for Akt phosphorylation. Scansite percentile scores, shown in the last column, represent substrates within the top percentage of potential Akt phosphorylation sites in the protein data bank. (b) Purified Akt phosphorylated GST-Cx43CT and GST-GSK3 (positive control), but not GST alone. Incorporation of radioactivity into the fusion proteins is shown in the upper part of the panel and the Coomassie stain of the gel is shown in the lower part of the panel. Akt also phosphorylated the GST-Cx43CT S373A mutant, consistent with a second target site for Akt at Ser369. Deletion of Ser368-Ile382 of Cx43 in the GST-Cx43CT mutant (GST-Cx43CT 368) significantly reduced phosphorylation by Akt. (c) The truncated mutant was recognized by a peptide antibody to residues 360-382, but not by a peptide antibody to residues 368-382 of Cx43, confirming the loss of the C-terminal amino acids in the fusion protein.
