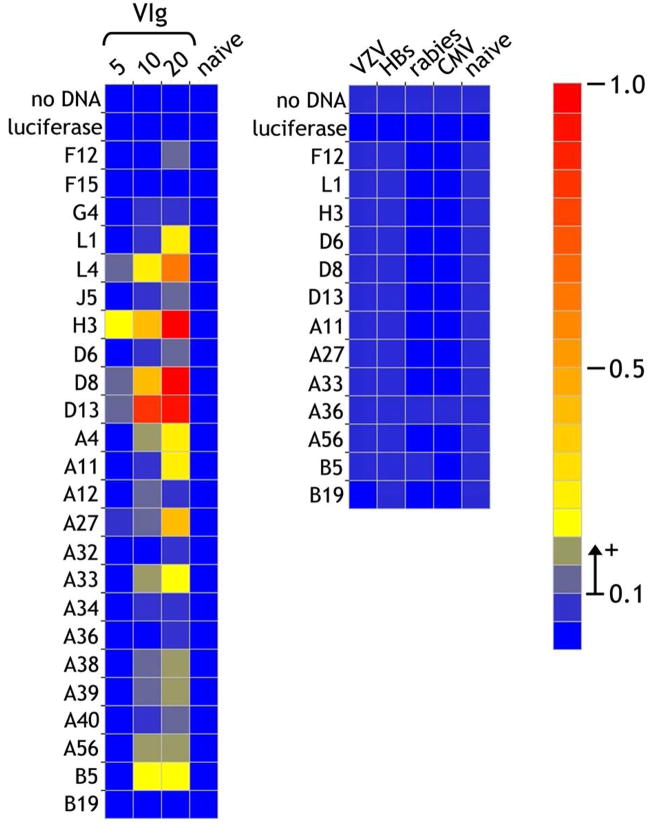
Figure 4. Detection of VIg antigenic reactivities using the ELISA protein array.
Vaccinia proteins produced by in transcription/translation in vitro were immobilized on neutravidin-coated plates through the biosynthetically-incorporated biotin tags. In the left-hand panel, VIg was incubated at 5, 10 and 20μg/ml and bound antibody detected by binding of anti-human IgG alkaline phospahatase activity. The highest concentration of 20μg/ml corresponds to a dilution of 1/2,500 from the stock. Immunoglobulin (20μg/ml) from a naïve individual was included as a control. As a further control for specificity, IgG from sera of individuals hyperimmunized against other microorganisms [varicella zoster (VZV), Hepatitis B secreted antigen (HBs), rabies and cytomegalovirus (CMV)] were also tested at 20μg/ml. The scale for the heatmap indicates optical density at 405nm detected in the ELISA assay. A value of >0.1 O.D. units above background was considered as significantly positive, while responses of 0.05–0.1 were considered borderline.