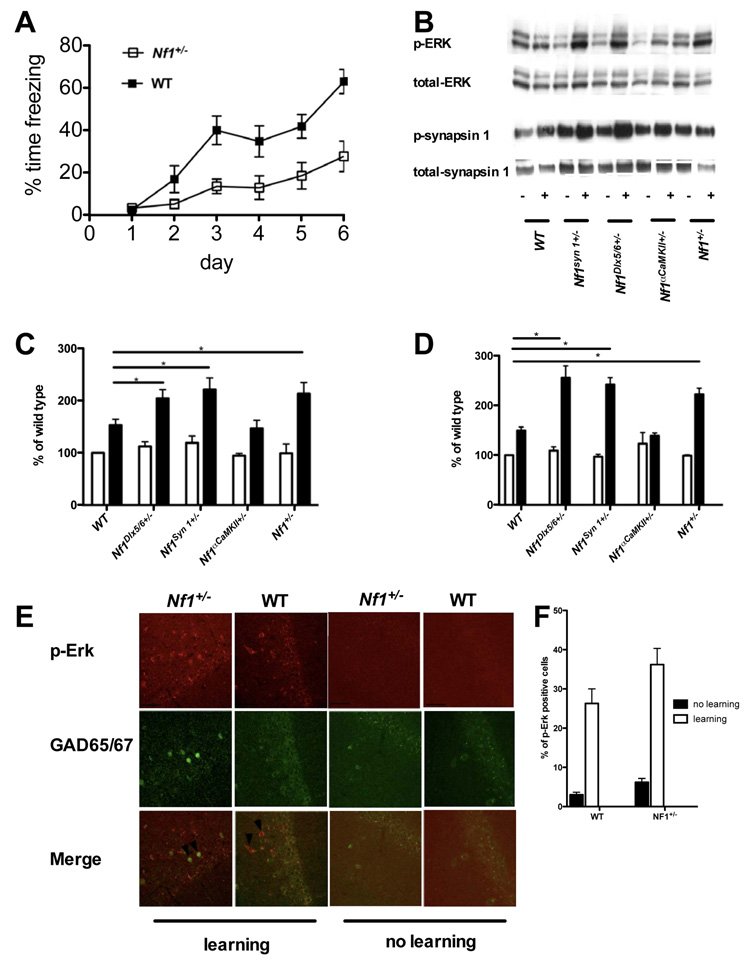
Figure 4. Increased ERK-dependent synapsin I phosphorylation in Cre-mediated Nf1 mutants.
A. Nf1+/− mice have deficits in the acquisition of contextual fear conditioning Nf1+/− mice (n=16) and WT controls (n=14) were trained with a contextual fear conditioning protocol using one-trial per day for 5 consecutive days. The average freezing levels during the first 30 seconds of each training day and 24 hours after the last training trial were plotted. WT mice freeze significantly more compare to WT (F(1,140)=3.927, P<0.05). Error bars indicate SEM. B. Contextual conditioning increases the phosphorylation of ERK and synapsin I (sites 4/5). Representative Western blots indicating protein bands visualized with antibodies to dually phosphorylated ERK1/2, total ERK1/2, synapsin I at sites 4/5, and total ERK1/2. + symbols denote contextual conditioning (shocks were delivered during the contextual exposure). - symbols denote that the no shock was delivered. C and D: Quantification of relative phosphorylated ERK1/2, synapsin I at sites 4/5; For each experiment, both phosphorylated and total MAPK levels were normalized to those observed in the control group of wild-type mice. 3–6 mice in each group. Values are mean ± SEM. E. Increased ERK phosphorylation in inhibitory neurons of Nf1+/−and WT mice after Morris water maze training After spatial learning, double immunofluorescent staining shows phosphorylated ERK (Red) in inhibitory neurons (labeled with GAD65/67, Green) of both WT and Nf1+/− mice. The arrows point to examples of neurons positive for both GAD65/67 and phosphorylated ERK in the hippocampal CA1 region of WT and Nf1+/− mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. F. Quantification of the relative number of ERK phosphorylation positive inhibitory neurons in the CA1 region of Nf1+/− mutants and WT controls. The overall number of ERK phosphorylation positive inhibitory neurons in the CA1 region is higher in Nf1+/− mutant (6.2±2.2%, n=4) mice than in WT controls (3.0±1.3%, n=4, t-test, p=0.0414); after 5 training trials in the Morris water maze, the numbers of ERK phosphorylation positive inhibitory neurons in the CA1 region increased in both Nf1+/− (36.2±9.21%, n=5) and WT (26.3±7.43%) mice.