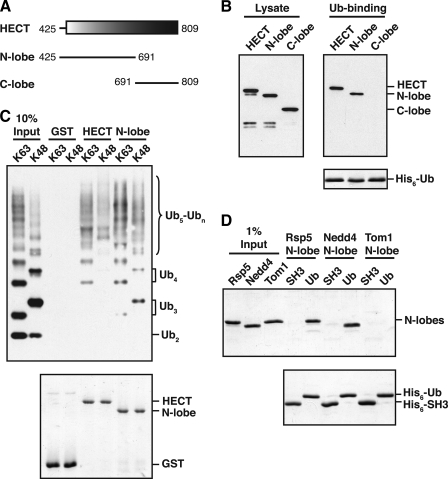
FIGURE 2.
The Rsp5 and Nedd4 HECT domain N-lobes bind to ubiquitin. A, schematic representation of the Rsp5 HECT domain. Fragments tested for ubiquitin binding in B are shown. B, bacterial lysates from cells expressing the indicated GST-tagged HECT domain fragments were incubated with beads carrying immobilized His6-tagged ubiquitin (His6-Ub). Lysates and proteins eluted from the beads were analyzed by anti-GST immunoblotting (top panels) or Coomassie staining (bottom panel). C, GST-HECT domain and GST-HECT N-lobe fusions were immobilized on beads, and the beads were incubated with purified His6-tagged Lys-63- or Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin chains. Purified chains (10% Input) and proteins eluted from the beads were analyzed by anti-His immunoblotting (top panel) or Coomassie staining (bottom panel). D, the indicated N-lobes were purified from an E. coli lysate and incubated with equivalent amounts of immobilized His6-Ub or a control His6-tagged SH3 domain from Rvs167 (His6-SH3). Purified N-lobes (1% Input) and proteins eluted from Ub or SH3 beads were detected by Coomassie staining.