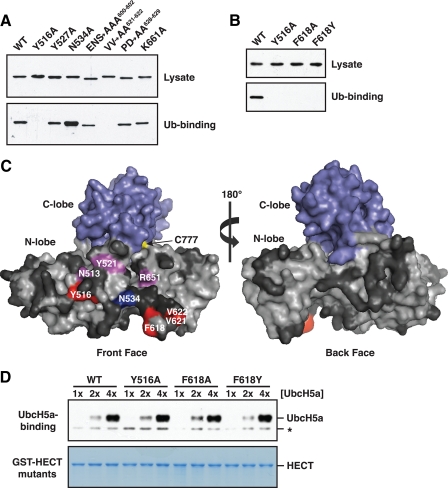
FIGURE 3.
Ubiquitin binds to a region on the front surface of the Rsp5 HECT domain N-lobe. A, a representative experiment from the alanine-scanning mutagenesis of residues in the Rsp5 HECT domain N-lobe. Bacterial lysates from cells expressing the indicated GST-tagged N-lobe mutants were incubated with beads carrying immobilized His6-tagged ubiquitin. Lysates and proteins bound to ubiquitin were analyzed by anti-GST immunoblotting. Mutation of the acidic residues in the E600A/N601A/S602A and P628A/D629A mutants resulted in slightly altered electrophoretic mobility. B, bacterial lysates from cells expressing the indicated GST-tagged HECT domain mutants were incubated with immobilized His6-tagged ubiquitin. Lysates and proteins bound to ubiquitin were analyzed by anti-GST immunoblotting. C, surface representation of the Rsp5 HECT domain, created by modeling onto the WWP1 HECT domain crystal structure (Protein Data Bank accession code 1ND7). Results of the alanine mutagenesis are summarized as follows: red, mutation abolished binding; magenta, mutation reduced binding; blue, mutation enhanced binding; dark gray, mutation had no effect. D, the indicated GST-HECT domain mutants were immobilized on beads, and the beads were incubated with increasing concentrations of purified UbcH5a: 25 (1×), 50 (2×), and 100 nm (4×). Proteins eluted from the beads were analyzed by anti-UbcH5a immunoblotting (top panel) or Coomassie staining (bottom panel). A nonspecific band unrelated to UbcH5a is represented by an asterisk.