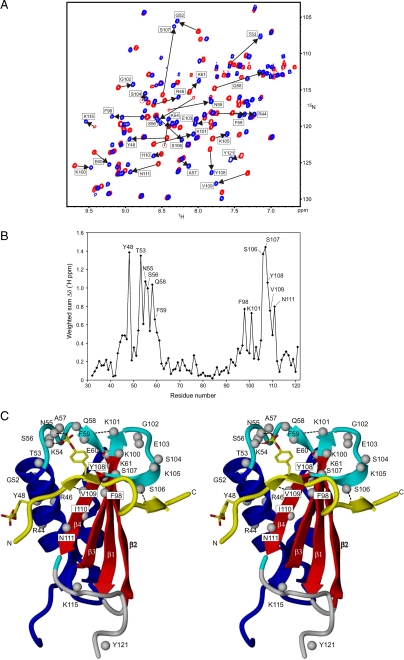
FIGURE 3.
Chemical shift perturbations of CHIPS31-121 upon complex formation with the C5aR peptide C5aR7-28S2. A, overlay of the 15N-1H HSQC spectrum of free uniformly 15N-labeled CHIPS31-121 (red) and of the titrated stoichiometric [15N]CHIPS31-121:C5aR7-28S2 complex (blue). Amide protons of CHIPS31-121 that experience substantial chemical shift perturbations (shown by the arrows) upon complex formation with C5aR peptide C5aR7-28S2 are labeled as such. B, weighted sum of CHIPS amide 15N-1H and 13Cα/β chemical shift changes, Δδ(1H ppm) = [(ΔδNH)2 + (0.25ΔδCα)2 + (0.25ΔδCβ)2 + (0.1ΔδN)2]1/2, upon binding the C5aR7-28S2 peptide, plotted versus residue number. Residues that were most affected are indicated by labels. Values for proline residues are based exclusively on carbon Cα/β shifts. C, side-by-side stereo cartoon representation of mapped positions within the CHIPS31-121 structure that display perturbed chemical shifts after formation of the CHIPS31-121:C5aR7-28S2 complex. Perturbed amide protons are indicated by gray balls. The peptide strand (colored yellow), running from residue 9-24 and including both sulfated tyrosines sY11 and sY14, is displayed as a visual reference of the binding interface. Broken lines indicate newly formed amide hydrogen bonds.