Figure 2.
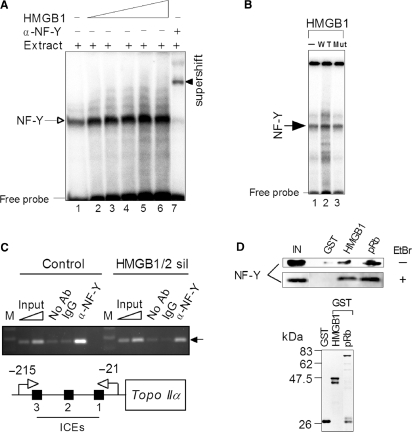
HMGB1 interacts with transcription factor NF-Y and modulates its binding to human topo IIα promoter. (A) HMGB1 enhances binding of NF-Y to ICE2. Radioactively labeled 30-bp DNA duplex containing ICE2 was mixed with nuclear extract from Saos-2 cells (lane 1) or nuclear extract containing increasing concentrations of HMGB1 (1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 μM, lanes 2-5, respectively), followed by separation of unbound ICE2 DNA duplex (free probe) and DNA–protein complexes on 5% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gels (EMSA). The presence of NF-Y within the retarded complex (arrow) was verified by super-shifting of the retarded complex (arrow head) with specific polyclonal antibodies against NF-YB. Specificity of NF-Y binding from nuclear extracts to DNA duplexes containing the wild-type ICE2 was also demonstrated by competition experiments with unlabeled DNA duplexes containing the wild-type or mutated sequence of the ICE2 (not shown). (B) HMGB1 mutant, incapable of DNA bending, cannot enhance binding of NF-Y to ICEs. EMSA experiment was carried out as in (A). Lane 1, no added HMGB1; lane 2, wild-type HMGB1 (2 μM); lane 3, HMGB1(F38A/F103A), 2 μM. Arrow indicate the mobility of (NF-Y)–DNA complexes. (C) ChIP assays using anti-NF-YB, control IgG antibodies or without antibodies were performed using chromatin from Saos-2 cells (control or upon silencing of HMGB1/2 expression, see Figure 6) as detailed in Materials and methods section. NF-Y binding to the topo IIα promoter was detected by gel staining (ethidium bromide) after PCR amplification using primers corresponding to the promoter as described in Materials and methods section. For semi-quantitative PCR, amplification reactions were carried out within the linear range of amplification (typically 30–34 cycles). The ChiP data were calculated as a ratio of PCR signal from ChIPed DNA to the input PCR signal, the final data were obtained from comparison of both cell lines (control or HMGB1/2 sil) and expressed as –fold change. Control, stably transfected Saos-2 cells (vector); HMGB1/2 sil, stably transfected Saos-2 cells with inhibited HMGB1/2 expression (shRNA-mediated gene silencing of HMGB1/2, Figure 6). The specific PCR product of 195-bp encompassing ICEs 1-3 is indicated by an arrow. M, DNA size marker; ICEs, inverted CCAAT elements. (D) Detection of NF-Y binding to HMGB1 or pRb in vitro. (Top) Equal amounts of GST, GST-HMGB1 or GST-pRb were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads and incubated with nuclear extract from Saos-2 cells. After extensive washings, the resin-bound proteins were eluted and separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by W. blotting and immunological detection by anti-NF-YB antibody as detailed in the Material and methods section. EtBr, ethidium bromide. IN, 25% of the nuclear extract from Saos-2 cells used for the ‘pull-down’ assay (input). (Bottom) GST or GST-tagged proteins immobilized on agarose beads for the ‘pull-down’assay (Coomassie blue R-250 staining).