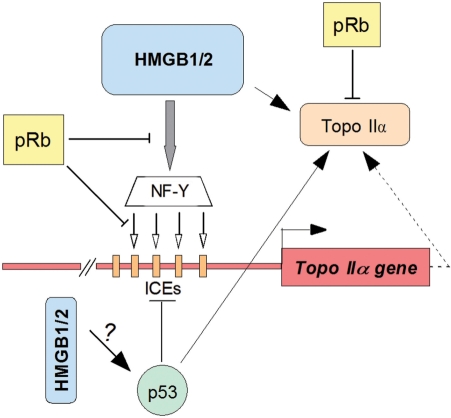
Figure 7.
Modulation of activity of human topo IIα gene and topoisomerase IIα by pRb and HMGB1/2 (a hypothesis). HMGB1 and HMGB2 proteins up-regulate the expression of the human topo IIα gene in pRb-negative cells by enhancement of binding of transcription factor NF-Y to its specific DNA-binding sites (ICEs) within the topo IIα gene promoter. Binding of NF-Y to the ICEs is facilitated by pre-bending the DNA sequences by HMGB1/2. pRb can inhibit the activity of the topo IIα gene, as well as the ability of HMGB1 to up-regulate the gene, possibly by reducing binding of NF-Y to ICEs (this article). HMGB1/2 promote cellular expression of topoisomerase IIα (this article), and the proteins have also the potential of enhancing catalytic activity of the enzyme, as previously demonstrated in vitro (11 and unpublished results). p53 inhibits activity of the topo IIα gene by compromising NF-Y binding (24,45). Unlike the inhibitory effect of pRb on the catalytic activity of topo IIα (22), the enzyme is stimulated by p53 (46).