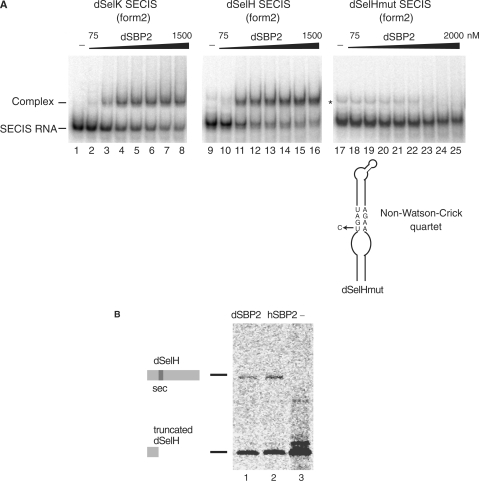
Figure 2.
Functional characterization of dSBP2. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed between the purified dSBP2 and the in vitro transcribed 32P-labeled form 2 SECIS RNAs (dSelK SECIS and dSelH SECIS) from Drosophila SelK and SelH selenoprotein mRNAs. Increasing concentrations (75–2000 nM) of dSBP2 were added. A dSeH mutant SECIS RNA (dSelHmut), carrying a U to C mutation in the non-Watson-Crick quartet, abolished the binding of dSBP2. dSBP2 was omitted in the control lanes 1, 9 and 17 (−). The asterisk denotes the position of a band that is also present in the control lanes 9 and 17. It often occurs and presumably contains an RNA conformer arising from T7 transcription. (B) dSBP2 can support selenoprotein H (dSelH) synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Synthesis of full-length (35S)-Met-labeled selenoprotein dSeH was obtained by adding purified dSBP2 (lane 1) or hSBP2 (lane 2) to the lysate. Lane 3: absence of SBP2 led to premature termination of translation (Truncated). Translation products were immunopurified and resolved by SDS–PAGE.