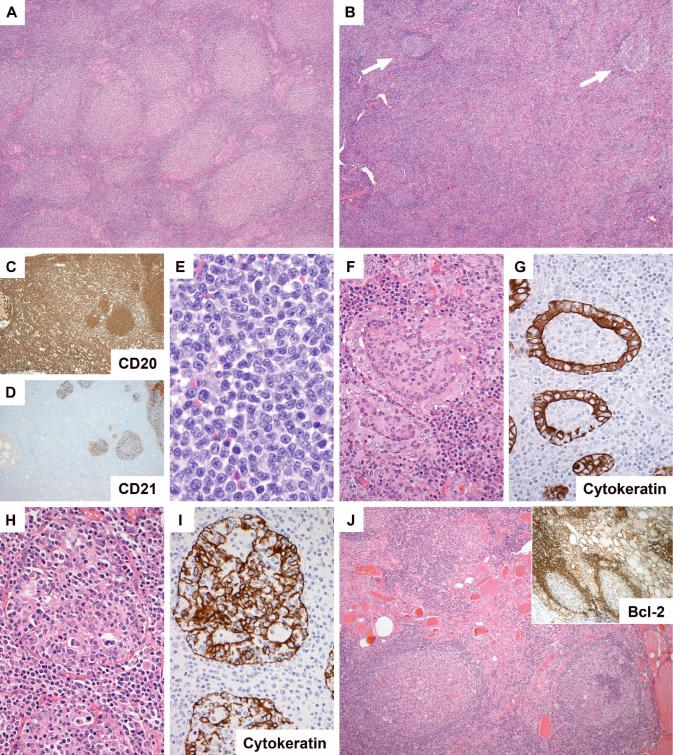
Figure 1.
Morphology of follicular lymphoma in the thyroid gland. In some areas/cases the neoplastic follicles were closely packed (A: H&E, case 2), while in several cases there were areas in which follicles (arrowed) were separated by expansive interfollicular neoplastic B cell infiltrates (B, case 16; C (CD20) and D (CD21), same area of case 10). The interfollicular cells were small centrocytic cells similar to those seen in the interfollicular region of nodal follicular lymphomas (E, case 18). Lymphoepithelial lesions were seen in all cases. These were of two overlapping types: those with intraluminal aggregates of neoplastic B cells (F and G (CD21), same area of case 13) and those with clusters of lymphocytes amongst hyperplastic epithelium (H and I (CD21), same area of case 16). Several cases contained foci of lymphocytic thyroiditis separate from the lymphoma (J, case 13).