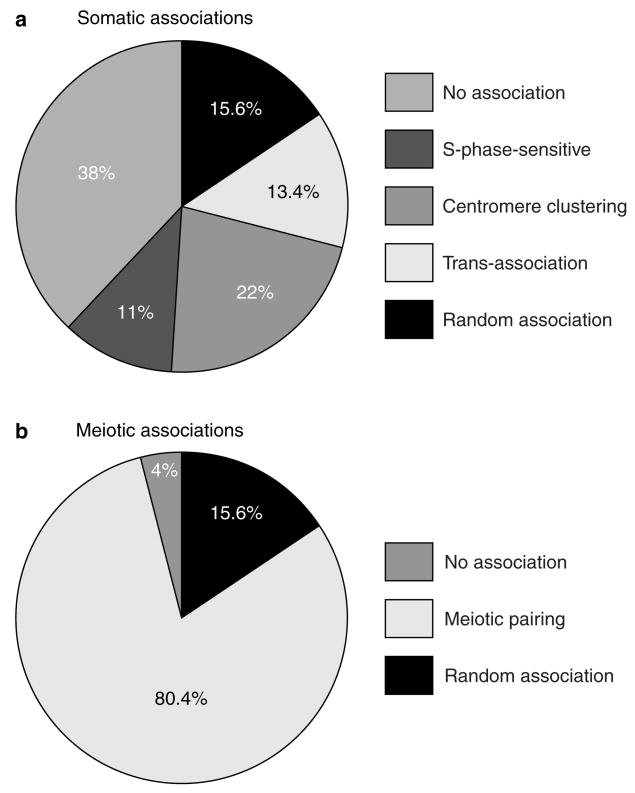
Figure 6. Dissection of somatic interchromosomal trans-association and meiotic homologue pairing.
a, Factors that contribute to somatic interchromosomal associations averaged for lacO–lacO interactions at allelic (trp1–trp1), and non-allelic centromere-linked (trp1–ura3) sites. Percentages were calculated as follows: random association, average lacO–tetO stochastic-collision values from ura3–trp1, ura3–met6 and ura3–ade8 associations (Fig. 5a); S-phase sensitive, subtraction of S values from G2/M values (Fig. 4g); centromere clustering, subtraction of G2/M values from G1 values (Fig. 4g); trans-association, average values obtained by subtracting lacO–tetO values from lacO–lacO values (Fig. 4g); no association, subtraction of G1 values from 100% (Fig. 4g). Some of the categories may overlap to some degree; for instance, both centromere clustering and trans-association may have an S-phase-sensitive component. b, Comparison of homologue and non-homologue interactions for meiotic cells. Percentages were calculated as follows: random, same values assumed as for a; no association, subtraction of lacO–lacO allelic pairing at t = 6 h from 100% (Fig. 3g); meiotic pairing, subtraction of random values from values for lacO–lacO allelic sites at t = 6 h (Fig. 3g).