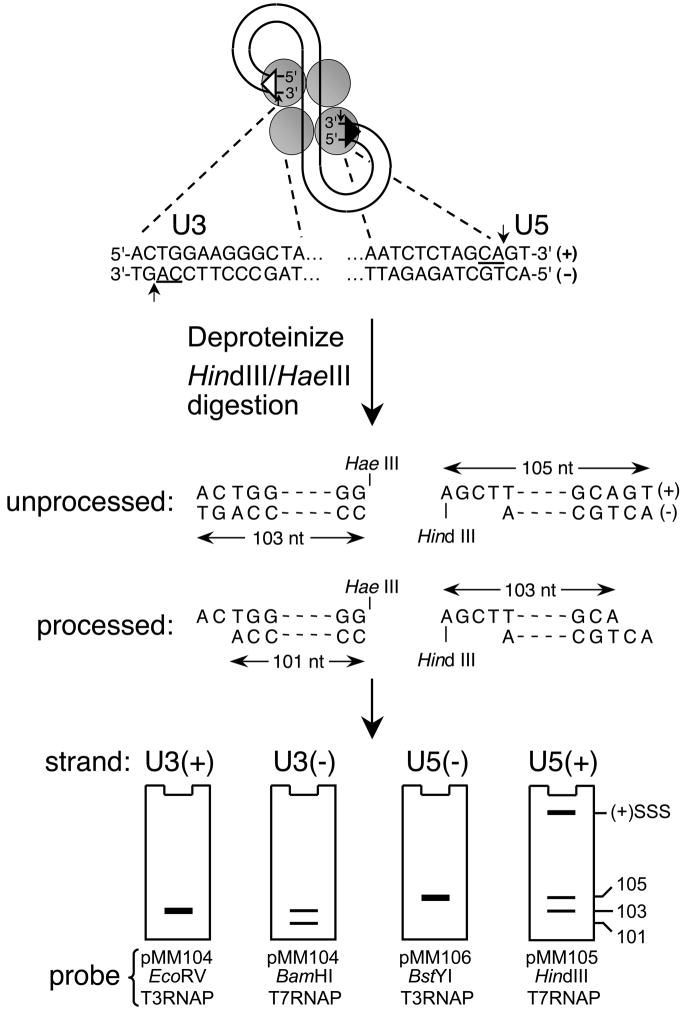
Fig. 2.
Indirect end-labeling of HIV-1 cDNA end structures. The terminal 13 bp of the U3 and U5 DNA att sites are shown beneath the HIV-1 PIC, with the phosphodiester bonds cleaved during 3′ processing and invariant CA dinucleotides marked by vertical arrows and underlines, respectively. The viral DNA ends are isolated as approximate 100 bp regions upon digestion with HindIII and HaeIII. The initial U3 minus-strand is 103 nucleotides, whereas integrase processing yields a 101 nt product. The unprocessed U5 plus-strand is 105 bases, with 3′ processing generating a shortened 103 nt strand. The U3 plus- and U5 minus-strands by contrast remain unchanged during 3′ processing. The various end structures are visualized by indirect end-labeling using riboprobes generated from the indicated linearized plasmid DNA templates, with the cartoon gels depicting the approximate mobilities of the different strands/3′ processing reaction products. (+)SSS, plus-strand strong-stop DNA; RNAP, RNA polymerase.