Figure 1.
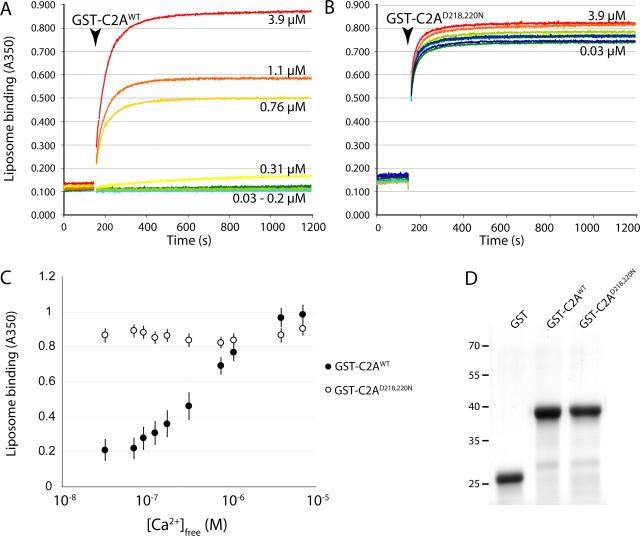
The C2A domain of DOC2B interacts with phospholipids in a calcium-dependent manner. A, B, Recombinant GST-C2A fusion protein was added to a mixture of Ca2+ and liposomes (arrowhead indicates the time of protein addition). Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding by the C2A domain, dimerized via the GST moiety, caused liposome aggregation, measured as an increase in absorption at 350 nm. Numbers in the graph correspond to the [Ca2+]free of calibrated Ca2+/EGTA solutions (blue to red colors indicate low to high [Ca2+]free). Liposome binding by GST-C2Awt was highly Ca2+ dependent (A), whereas GST-C2AD218,220N showed Ca2+-independent binding (B). C, Summary of data showing the calcium dose dependence of phospholipid binding (average ± SEM; n = 8). D, Recombinant GST-C2Awt and GST-C2AD218,220N appeared similar in SDS-PAGE. The positions of molecular size markers are indicated at the left. GST alone did not induce any liposome aggregation (data not shown).