Abstract
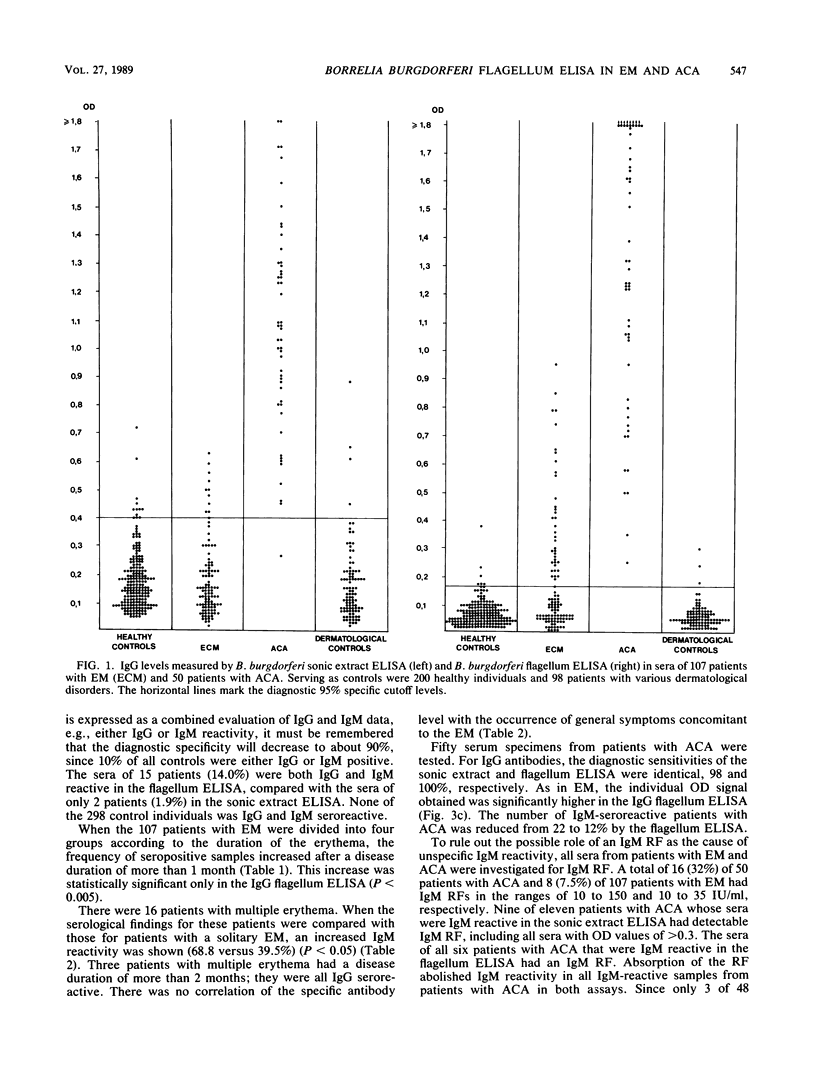
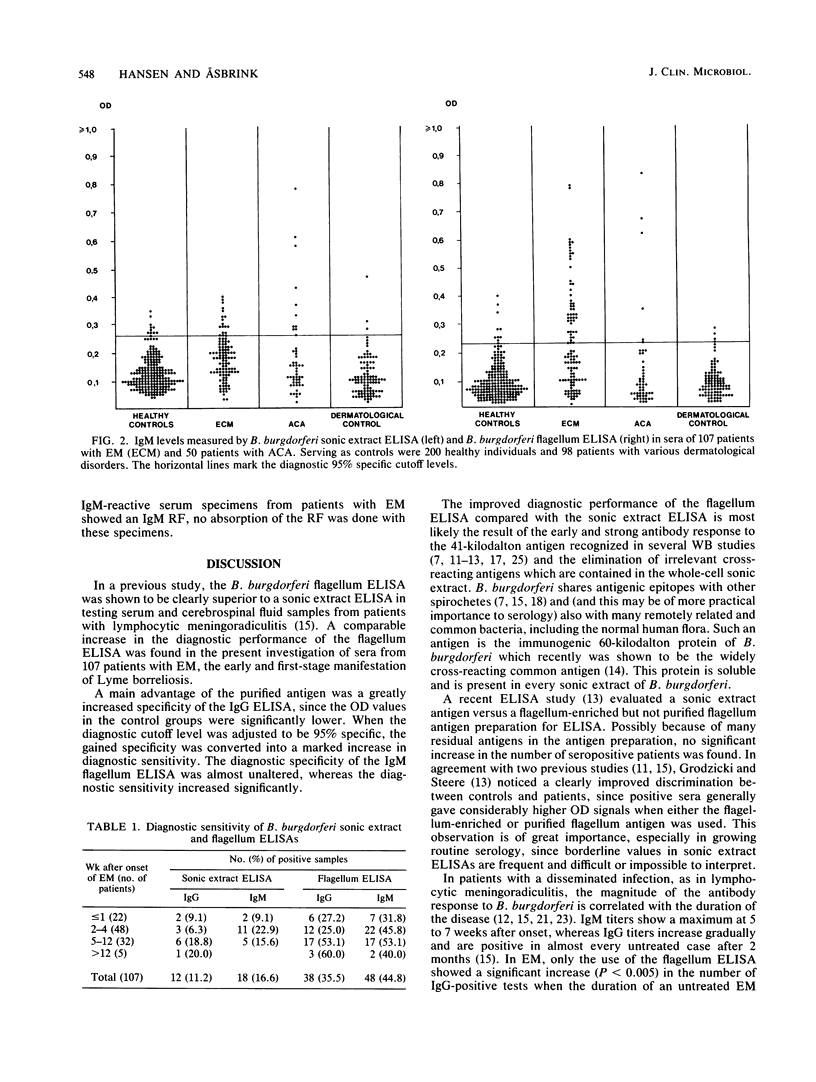
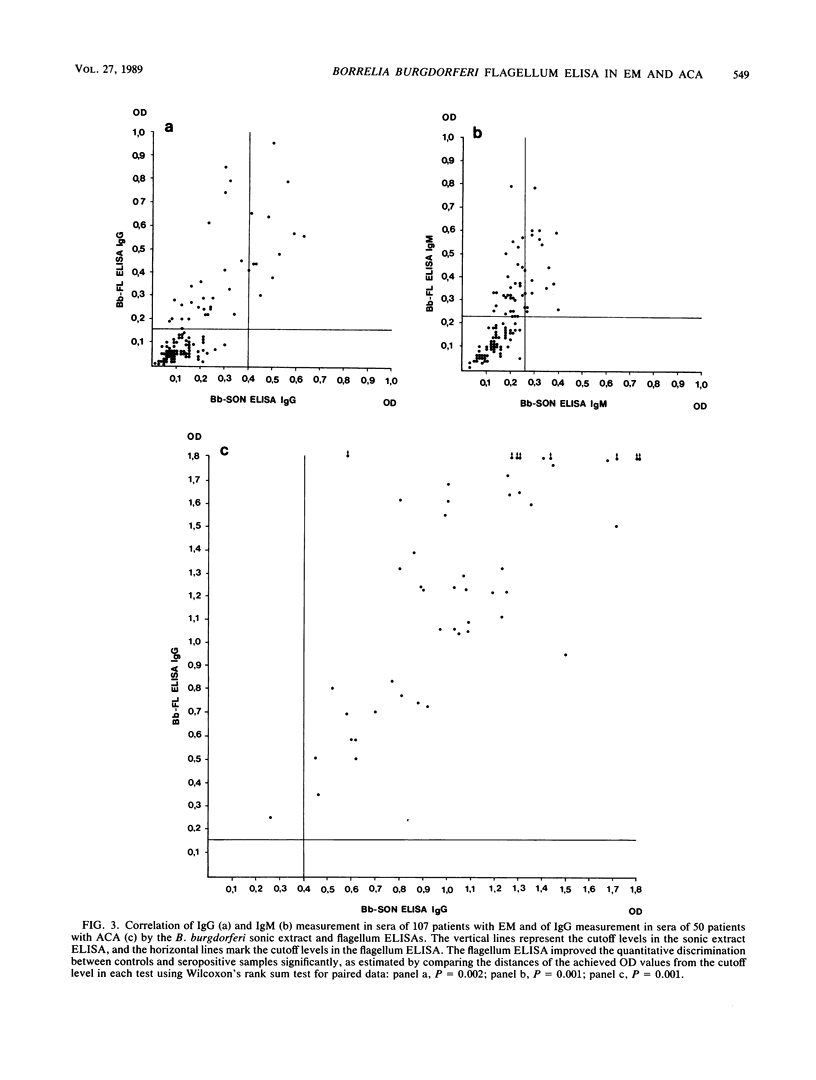
The diagnostic performance of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using purified Borrelia burgdorferi flagella as test antigen was compared with that of a B. burgdorferi sonic extract ELISA. We tested sera from 200 healthy controls, 107 patients with erythema migrans (EM), 50 patients with acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA), and 98 patients with various dermatological disorders without clinical evidence of active Lyme borreliosis. The flagellum ELISA was significantly more sensitive than the sonic extract ELISA. With sera from patients with EM, the diagnostic sensitivity for immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody detection increased from 11.2 to 35.5% (P less than 0.001) and for IgM antibody detection it increased from 16.6 to 44.8% (P less than 0.001). In the flagellum ELISA, the number of positive tests increased significantly (P less than 0.005) when the duration of EM exceeded 1 month, but still only about 50% of patients with longstanding (1 to 12 months) untreated EM were IgG seropositive. Concomitant general symptoms did not affect the antibody level, whereas patients with multiple erythema were more frequently seropositive. All sera from patients with EM which were positive in the sonic extract ELISA were also positive in the flagellum ELISA. Not only did the overall number of positive tests increase, but the flagellum ELISA yielded a significantly better quantitative discrimination between seropositive patients and controls (P less than 0.002). IgG antibodies to the B. burgdorferi flagellum were found in all sera from patients with ACA, indicating persistence of an antiflagellum immune response in late stages of Lyme borreliosis. IgM reactivity in sera from patients with ACA was shown to be unspecific and the result IgM rheumatoid factor. A rheumatoid factor was detected in sera from 32% of patients with ACA, compared with 7.5% of patients with EM. The improved diagnostic performance, the ease of standardization of the flagellum antigen, and the lack of strain variation make the B. burgdorferi flagellum a needed reference antigen for growing routine serology in Lyme borreliosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann R., Kabatzki J., Boisten H. P., Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Hartung S., Runne U. Spirochäten-Atiologie der Erythema-chronicum-migrans-Krankheit. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1984 Jan 20;109(3):92–97. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Brehmer-Andersson E., Hovmark A. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans--a spirochetosis. Clinical and histopathological picture based on 32 patients; course and relationship to erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986 Jun;8(3):209–219. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198606000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hederstedt B., Hovmark A. The spirochetal etiology of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius. Acta Derm Venereol. 1984;64(4):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A., Hederstedt B. Serologic studies of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans with indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65(6):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A., Hederstedt B. The spirochetal etiology of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans Herxheimer. Acta Derm Venereol. 1984;64(6):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Hindersson P., Pedersen N. S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.338-346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høier-Madsen M., Nielsen L. P., Møller S. Bestemmelse af IgM-rheumafaktorer ved enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Ugeskr Laeger. 1986 Aug 4;148(32):2018–2021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell H., Sampson J. S., Schmid G. P., Wilkinson H. W., Plikaytis B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha M., Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Diagnosing early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90432-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G. T., Granström M., Hederstedt B., Sköldenberg B. Diagnosis of spirochetal meningitis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):819–825. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.819-825.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiernstedt G., Eriksson G., Enfors W., Jörbeck H., Svenungsson B., Sköldenberg B., Granström M. Erythema chronicum migrans in Sweden: clinical manifestations and antibodies to Ixodes ricinus spirochete measured by indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Scand J Infect Dis. 1986;18(3):217–224. doi: 10.3109/00365548609032330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Schierz G., Preac-Mursic V., Weber K., Pfister H. W., Einhäupl K. Serological diagnosis of erythema migrans disease and related disorders. Infection. 1984 Sep-Oct;12(5):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01651147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


