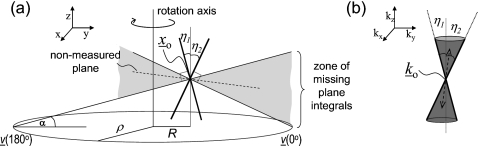
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic representation of missing plane information at point xo. Shaded area indicates the region of missing planes with normal vectors restricted to the y–z plane for simplicity. An example of a nonmeasurable plane is indicated by the dashed line. (b) Missing plane information results in unmeasured lines of spatial frequencies that fill a cone in the local Fourier domain as illustrated where ko corresponds to the DC (zeroth frequency) component. The minimum, η1 and maximum, η2, internal angles of the missing cone are shown in (a) as they relate to the x-ray cone angle, α, at source position ν(ϕ), where ϕ is the transverse angle in degrees, measured counterclockwise from the x axis.