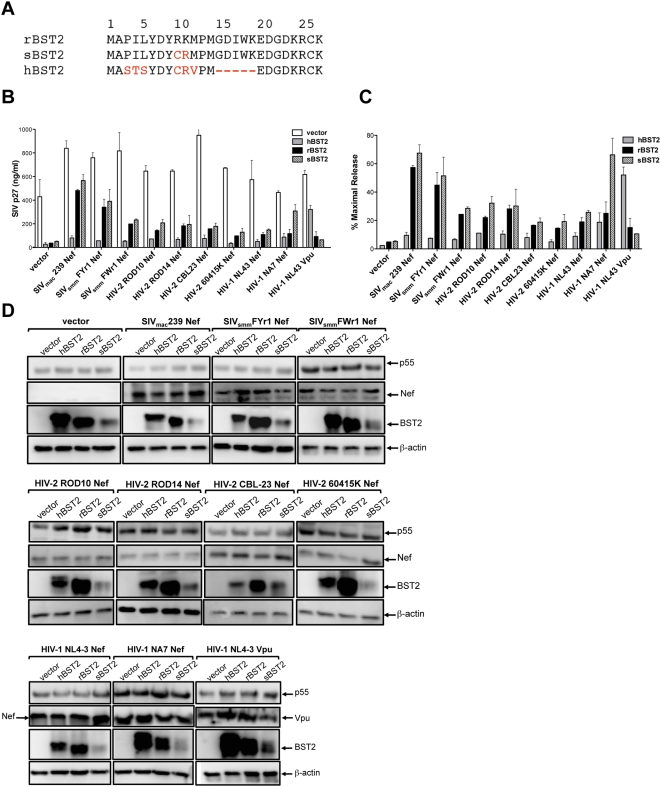
Figure 9. Nef alleles of SIVsmm/mac, HIV-2 and HIV-1 counteract rhesus macaque and sooty mangabey tetherin, but not human tetherin.
Nef alleles of SIVsmm/mac, HIV-2 and HIV-1 were tested for the ability to rescue particle release for SIV Δnef in the presence of human tetherin (hBST2), rhesus macaque tetherin (rBST2) and sooty mangabey tetherin (sBST2). (A) The amino acid sequences corresponding to the cytoplasmic domains of hBST2, rBST2 and sBST2 are shown. Dashes represent sequence gaps and residues that differ from rBST2 are indicated in red. The mean and standard deviation (error bars) for total p27 release (B) and for percent maximal release (C) are shown for the indicated Nef alleles of SIVsmm/mac, HIV-2 and HIV-1 in the presence of hBST2, rBST2 and sBST2. (D) Protein expression was confirmed for SIV p55 Gag, BST2, HIV-1 Vpu and for each of the Nef alleles by western blot analysis of 293T cell lysates. The Nef proteins of SIVmac239 and SIVsmm (FYr1 and FWr1) were detected using plasma pooled from SIV-infected rhesus macaques and SIV-infected sooty mangabeys respectively. The Nef proteins of HIV-2 ROD10, ROD14, CBL-23 and 60415K were detected using plasma pooled from HIV-2-infected individuals. The Nef proteins of HIV-1 NL4-3 and NA7 were detected using polyclonal rabbit antisera. SIV p55 Gag, BST2 and β-actin were detected with the monoclonal antibodies 183-H12-5C, HM1.24 and C4. Following incubation with an appropriate HRP-conjugated secondary antibody, the blots were developed in chemiluminescent substrate and visualized using a Fujifilm Image Reader LAS 3000.