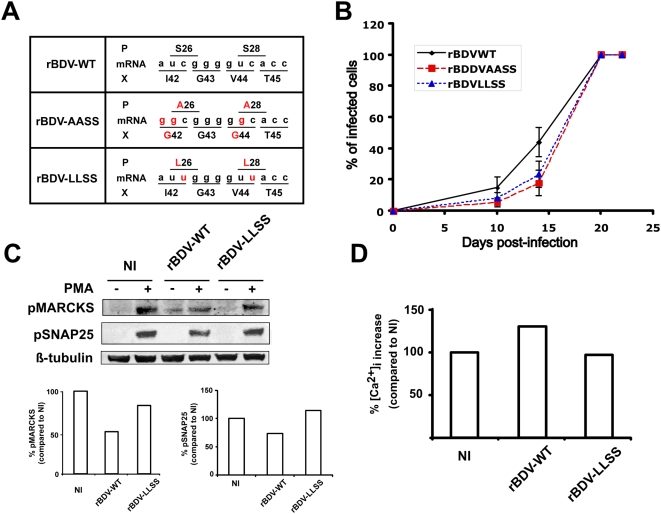
Figure 4. Phenotypic characterization of a recombinant BDV (RBDV-LLSS) bearing mutations in the PKC phosphorylation site of P (S26L;S28L), but none in the overlapping X protein.
(A) Cartoon depicting part of the P and X overlapping open reading frames of the 0.8 kb mRNA from the indicated viruses and their translation products. Amino acids and nucleotides highlighted in red indicate differences from the wild-type situation. (B) Comparative analysis of virus spread for rBDV-wt, rBDV-AASS and rBDV-LLSS recombinant viruses. Percentages of BDV positive neurons were assessed by immunofluorescence on different days of culture, as described in Figure 1. This measure was carried out on two replicate wells for each time point, after random selection of five different fields for each replicate. Results are expressed as mean±s.e.m. of three independent experiments. (C) Analysis of PKC signaling in hippocampal neurons. Total extracts were prepared from non-infected (NI) neurons and neurons infected with the rBDV-WT or rBDV-LLSS viruses (21 days post-infection), after stimulation or not with 1 µM PMA for 10 min. Equivalent protein amounts were analyzed by Western blot with specific antibodies for phospho-MARCKS and phospho-SNAP-25. ß-tubulin was used to normalize expression. Bottom graphs show the fluorometric quantification, using the Odyssey imager, of one representative experiment out of three. Quantification results were expressed as percentage of increase relative to the response of NI neurons, which was set at 100%. (D) Quantitative analysis of peak calcium responses recorded from hippocampal neurons infected with the rBDV-WT and rBDV-LLSS viruses. In each case, recordings were performed on six separate wells, and data represent results of a representative experiment out of two. [Ca2+]i increase was expressed as the increase in fluorescence signal after stimulation relative to the increase measured in control neurons, which was set at 100%.