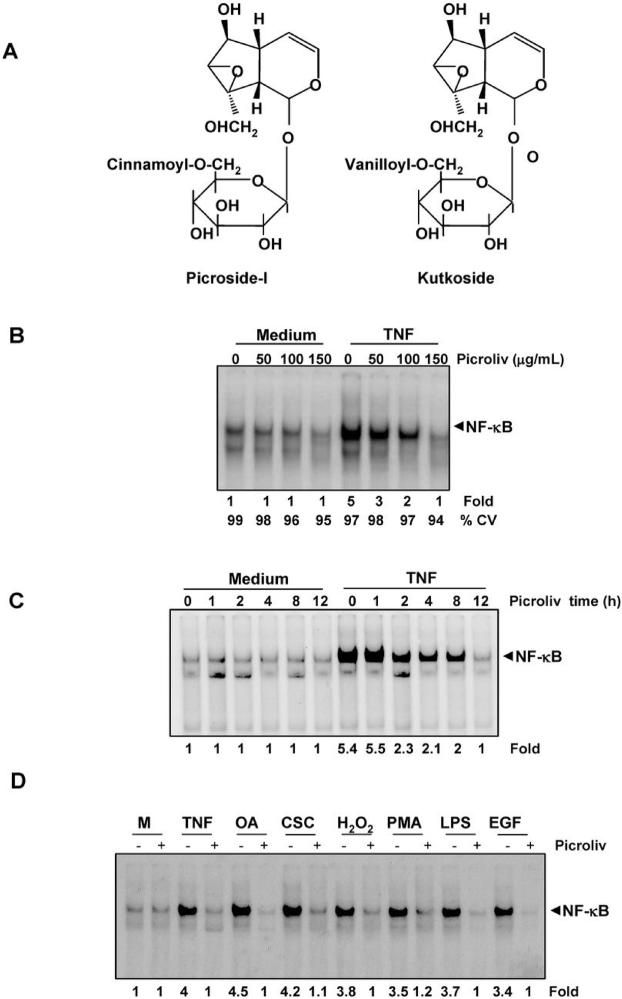
Figure 1.
A, structure of picroside-I and kutkoside. B, Picroliv suppresses TNF-induced NF-κB activation in a dose-dependent manner. KBM-5 cells (2 × 106) were incubated with picroliv at different concentrations for 12 h and then treated with TNF (0.1 nM) for 30 min. Nuclear extracts of the cells were prepared and assayed for NF-κB activation using EMSA. Cell viability was measured by trypan blue assay. C, Picroliv suppresses TNF-induced NF-κB activation in a time-dependent manner. KBM-5 cells (2 × 106) were incubated with 150 μg/mL picroliv for the indicated time periods and then treated with TNF (0.1 nM) for 30 min. Nuclear extracts of the cells were then prepared and assayed for NF-κB activation using EMSA. D, Picroliv blocks activation of NF-κB induced by TNF, OA, CSC, H2O2, PMA, LPS, and EGF. KBM-5 cells (2 × 106) were preincubated with 150 μg/mL picroliv at 37°C for 12 h and then treated with TNF (0.1 nM, 30 min), OA (500 nM, 4 h), CSC (10 μg/mL, 1 h), hydrogen peroxide (500 μM, 2 h), PMA (25 ng/mL, 1 h), LPS (100 ng/mL, 2 h), and EGF (100 ng/mL, 2 h). Nuclear extracts were prepared and assayed for NF-κB activation using EMSA (M, medium).