Figure 1.
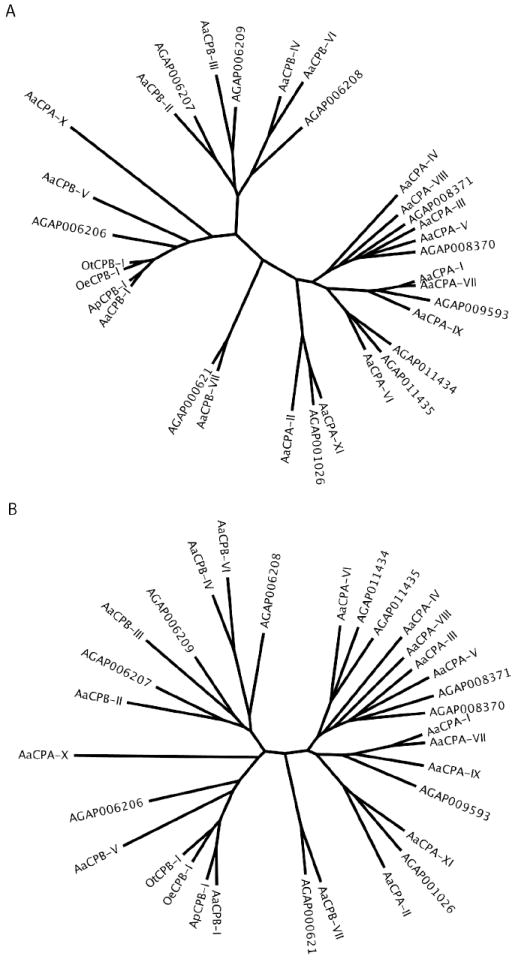
Phylogenetic analysis of amino acid and nucleotide sequences of mosquito carboxypeptidases belonging to the M14 family of zinc-metallopeptidases. A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of 32 carboxypeptidase genes based on amino acid sequences derived from the mature peptide, omitting the signal and propeptide regions. Multiple sequence alignments were first prepared by ClustalW based on nucleotide sequences encoding the mature peptide. The aligned nucleotide sequences were then converted into deduced amino acid residues, and the protein sequences were re-aligned by ClustalW using SeaView software (see supplemental figure 1). B) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of the same 32 carboxypeptidase genes as in “A,” based on the corresponding nucleotide sequences derived from the mature peptide. The five mosquito species used in these analyses are Ae. aegypti (Aa), An. gambiae (AG), Ae. polynesiensis (Ap), Oc. triseriatus (Ot), and Oc. epactius (Oe).
