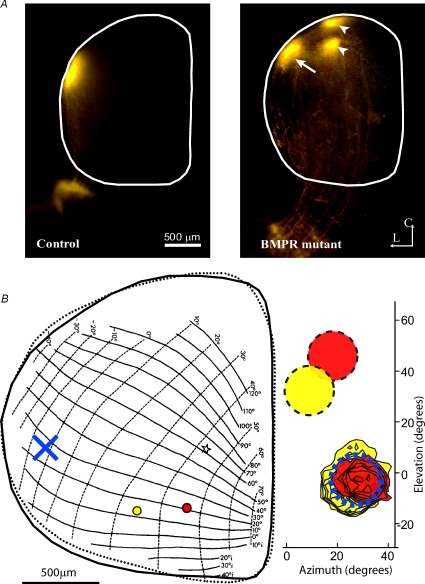
Figure 2. Ventralization of retinal axons in BMPR mutant mice.
A, focal dorsal retinal injection in control animal results in a focal termination zone at the lateral edge of the colliculus (left). A similar focal injection in a BMPR mutant mouse (right) results in a normal target zone in lateral colliculus (arrow) as well as 2 additional ectopic target zones shifted medially (arrowheads). The SC is outlined in white. L is lateral, C is caudal. B, Drager's map of visual space (left, from Drager & Hubel, 1976) in the SC overlaid with an outline (continuous line) of the SC from an example BMPR mutant mouse. Indicated in red and yellow are the locations of two electrode penetrations yielding corresponding receptive fields that overlap in visual space (contoured red and yellow RFs overlap; right). Indicated by yellow and red discs (right) are the response regions in visual space predicted for control neurons. Indicated as a blue X (left) is the location in a control SC that has a RF centred at the location where the 2 ectopic RFs are. This result illustrates the physiological manifestation of an anatomical ectopic spot in the BMPR mutant, with two different regions in the retina projecting to the same ectopic region in the SC.