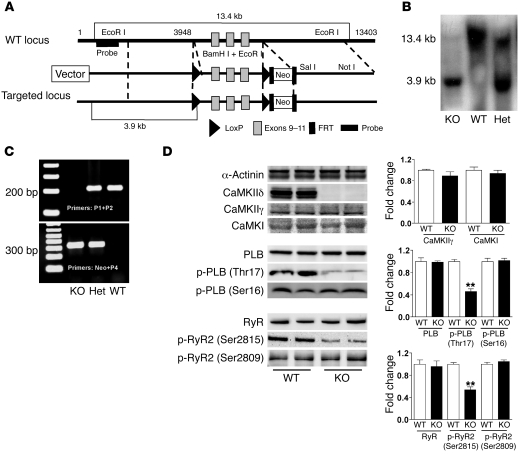
Figure 1. Generation and characterization of mice with CaMKIIδ deletion.
(A) Restriction map of the genomic structure of the Camk2d gene, the targeting construct, and the mutated locus after recombination. The targeting construct was generated by flanking exons 9–11 of Camk2d with 2 loxP sites and flanking the Neo cassette by Flp recombinase target (FRT) sites. (B) Genotyping of CaMKIIδ-deficient mice by Southern blot analysis with the probe shown in A. Genomic DNA was isolated from the tails of a WT, a KO, and a heterozygous (Het) mouse. The 13.4- and 3.9-kb bands represent WT and mutant alleles, respectively. (C) Genotyping of KO mice by PCR analysis using mouse tail DNA and specific primers for the WT (P1+P2) and mutant (Neo+P4) alleles. (D) Analysis of protein expression and phosphorylation in WT and CaMKIIδ-deficient mice. LV homogenates were subjected to Western blotting. Quantitative analysis of the expression and phosphorylation of the proteins is shown at right. Data are mean ± SEM of 4–7 determinations. **P < 0.01 versus WT.