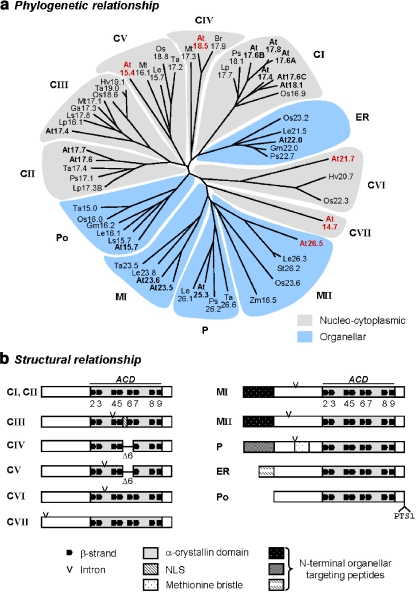
Fig. 1.
Classification and basic structures of plant sHsps. a Phylogenetic tree of plant sHsps based on sequence alignment of amino acid residues forming the α-crystallin domain (ACD). A. thaliana sHsps are in bold, and the newly identified members are highlighted in red. In total, 12 sHSP subfamilies are defined, i.e., seven cytoplasmic/nuclear subfamilies CI to CVII, one subfamily each of proteins targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), plastids (P), and peroxisomes (Po), respectively, and the two mitochondrial subfamilies MI and MII. b Block diagrams illustrate common and subfamily-specific elements of sHsp structures based on protein sequence alignments and secondary structure predictions. Size variations in the N- or C-terminal regions extending from the ACD are ignored. Predicted β-strands (β2–β9) are numbered according to the crystal structure of wheat Hsp16.9-CI. Amino acid residues involved in β6 formation are lacking in CIV and CV members (Δ6). Intron positions at the nucleotide level, targeting sequences, and the methionine bristle of the plastidial sHsps are indicated. For sequence alignments of the newly defined sHsp subfamilies, see Fig. S1. Data base accession numbers are given in Table S3. At Arabidopsis thaliana, Br Brassica rappa, Ga Gossypium arboretum, Gm Glycine max, Hv Hordeum vulgare, Le Lycopersicon esculentum, Lp Lycopersicon peruvianum, Ls Lactuca sativa or L. serriola, Mt Medicago truncatula, Os Oryza sativa, Ps Pisum sativum, St Solanum tuberosum, Ta Triticum aestivum, Zm Zea mays