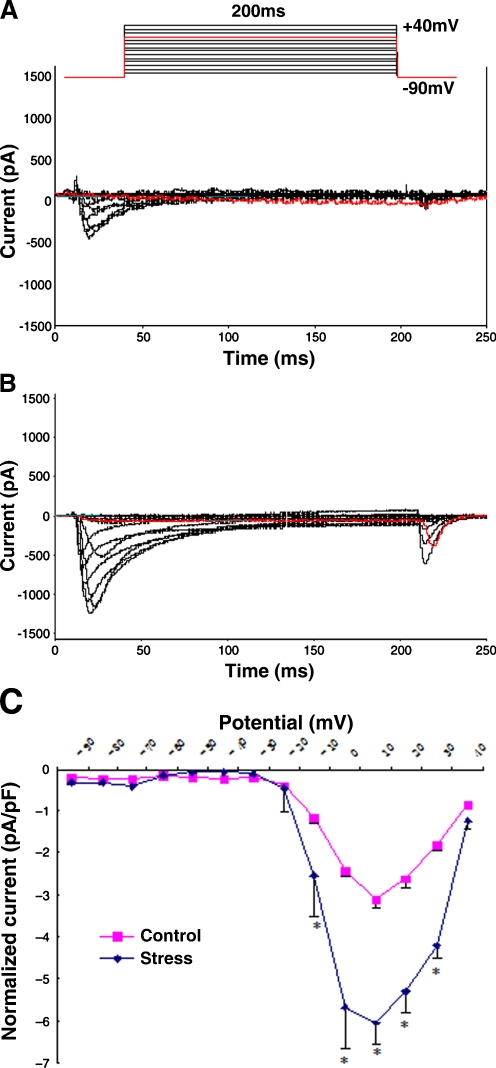
Fig. 2.
Alterations of ICa-L in rat ventricular myocytes under chronic restraint stress. A, B. Representative ICa-L traces for control and chronic stress. Superimposed ICa-L were elicited from a holding potential of −90 mV to test potential ranging from −80 to +40 mV in 10 mV increment steps for 200 ms using the whole-cell patch clamp technique. The voltage-clamp protocol is shown schematically above the traces. The amplitude of peak ICa-L at all test potential was larger in the ventricular myocytes isolated from chronic stress rats (B) than control (A). C Current density versus voltage relationship of mean peak ICa-L for control and chronic stress cells. The peak ICa-L recorded at each step of the voltage pulse protocol is plotted as a function of the voltage step to construct the current–voltage relationship. To account for cell size, current density (pA/pF) was determined by dividing current amplitude by cell capacitance (an index of cell surface area). Current density increased markedly in ventricular myocytes obtained from chronic stress (−6.04 ± 0.98 pA/pF, n = 6) rats compared to control (−3.13 ± 0.02 pA/pF, n = 6, P < 0.05)