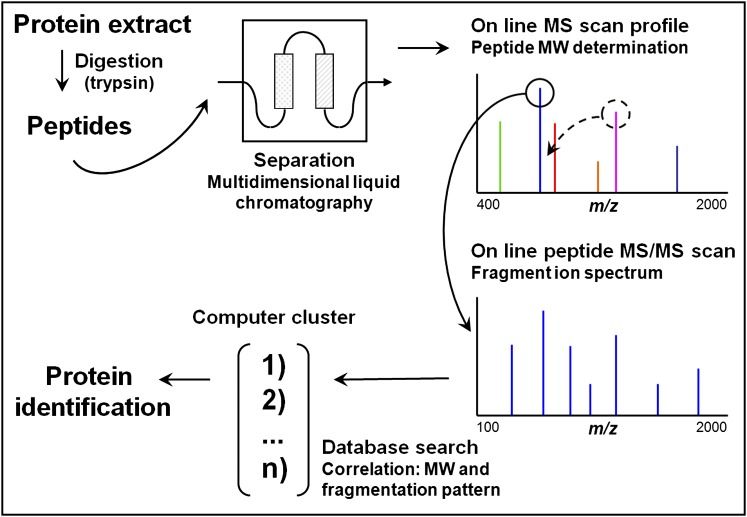
Figure 2.
Bottom up or shotgun protein identification by liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectrometry (MS)/MS from a complex protein mixture. The protein mixture is first digested (by trypsin) and the resulting peptides are separated by multidimensional liquid chromatography (typically strong cation exchange followed by reverse-phase separation) coupled online to the mass spectrometer. As they elute, the m/z ratios of the peptides are first determined followed by one or several MS/MS scans from the most abundant peptide signals. This cycle is repeated until all of the peptides have eluted from the chromatography column. For each precursor peptide selected for MS/MS, peptides of similar nominal mass are extracted from sequence databases and predicted fragmentation patterns are derived in silico. These patterns are then compared with the experimental fragmentation spectrum to generate correlation scores. Positive identification of a protein is based on the observation of two or more peptides issued from its sequence. Modified by permission from Reference 131.