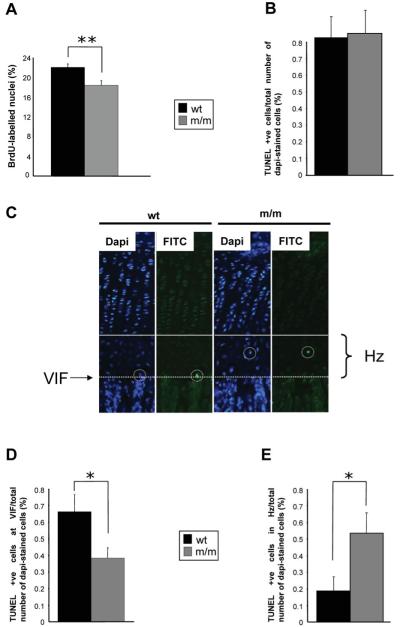
Figure 7.
Cell proliferation and apoptosis are significantly affected in the mutant growth plate. (A) Twenty-one day old mice were administered with 0.01 ml/g of the nucleotide analogue BrdU 2 h prior to sacrifice. Tibia samples from mice were processed as normal and IHC was performed using anti-BrdU antibody on ethanol-fixed 6 μm sections. The proportion of BrdU-labelled nuclei was calculated by comparing the number of BrdU-labelled nuclei with the total number of chondrocytes in the proliferating zone (i.e. methyl green-labelled nuclei + BrdU-labelled nuclei). Mice homozygous for the matn3 p.V194D mutation had significantly lower proliferation rates when compared with wild-type and heterozygote mice (n > 36 section per genotype, independent t-test, **P < 0.01). End-stage apoptosis (DNA fragmentation) was measured in the tibia of 21-day-old mice (PFA-fixed 6 μm sections) using the DeadEnd™ fluorometric TUNEL system. (B) The relative levels of apoptosis were calculated by comparing the number of apoptotic chondrocytes (FITC-labelled nuclei) with the total number of chondrocytes in the hypertrophic zone (DAPI-labelled nuclei + FITC-labelled nuclei). (C) Representative images of tibia growth plates showing DAPI and FITC stained sections. White circles highlight TUNEL-positive chondrocytes while the solid line indicates the start of the hypertrophic zone and the dotted line marks the VIF. Apoptosis was occurring away from the VIF in mice homozygous for the mutation. (D) The rate of apoptosis at the VIF for mice homozygous for the mutation was 0.38% when compared with 0.66% for wild-type mice; an overall reduction of >40% (E) Apoptosis of chondrocytes in the hypertrophic zone was significantly increased in mutant mice (n > 20 sections per genotype, independent t-test, **P < 0.05).