Fig. 10.
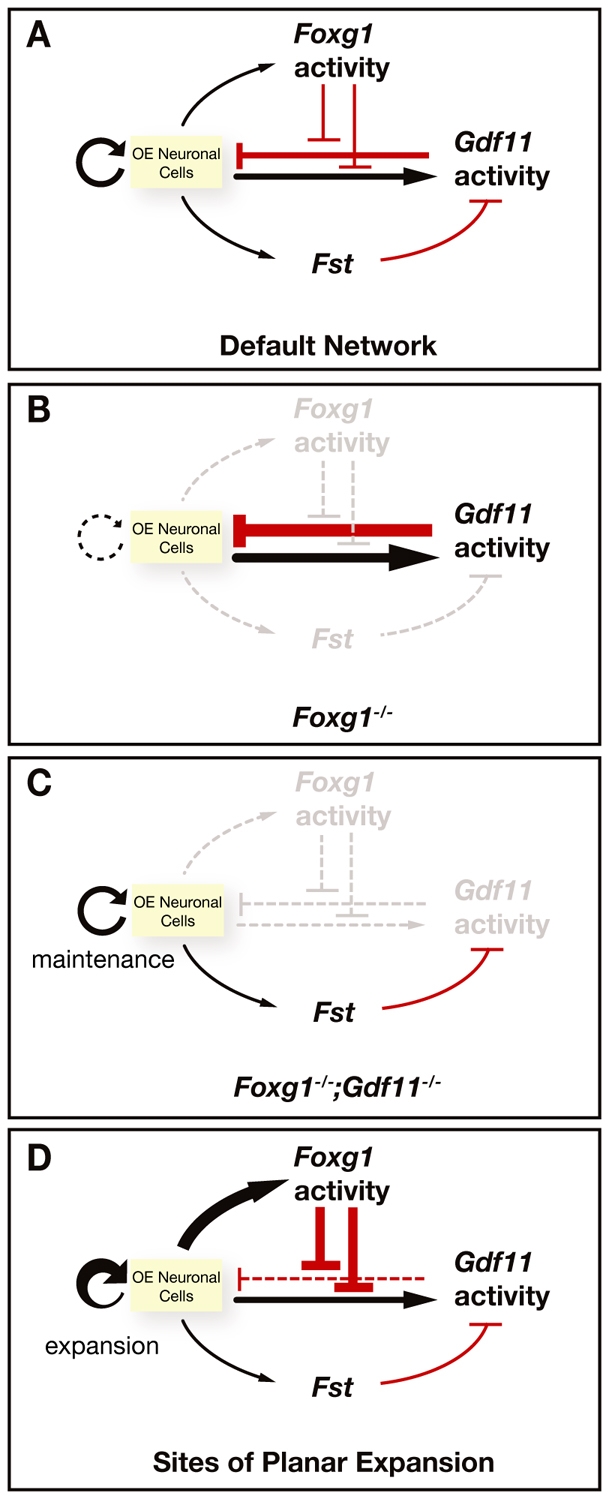
Schematic model of Foxg1-Gdf11 interactions controlling OE neurogenesis. (A) In wild-type OE, Foxg1 and Gdf11 are both produced by OE neuronal cells, but Foxg1 pro-neurogenic activity antagonizes both the anti-neurogenic activity of Gdf11 and the production of Gdf11 by OE neuronal cells. Fst is also expressed by OE neuronal cells, and Fst action antagonizes Gdf11 activity. This default network of gene activities controls the normal steady-state level of neurogenesis in the OE. (B) In Foxg1-/- OE, Foxg1 activity is absent, Fst expression is downregulated, and Gdf11 expression is upregulated, resulting in hypersensitivity of the frontonasal region and OE to the action of Gdf11. Both OE neurogenesis and planar expansion of the OE fail. (C) In the Foxg1-/-;Gdf11-/- double mutant, Fst expression is restored and histogenesis (neurogenesis) within the OE is rescued, as the anti-neurogenic activity of Gdf11 is now removed and any similar anti-neurogenic factors are antagonized by Fst. (D) Foxg1 activity strongly inhibits both Gdf11 activity and expression, which would allow the OE to undergo planar expansion in sites where Foxg1 is highly expressed in wild-type OE (e.g. posterior recess of the nasal cavity). Once expansive growth is finished, Foxg1 expression is downregulated (e.g. in the anterior septum), and OE neurogenesis returns to its default state.
