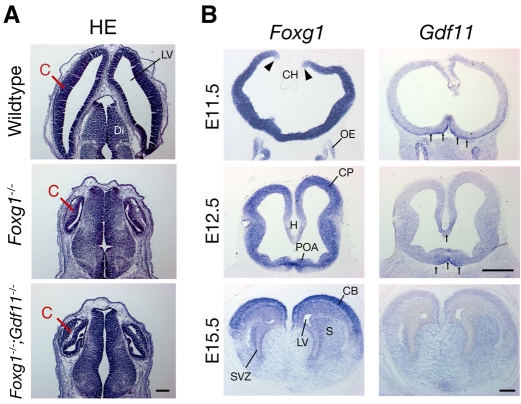
Fig. 9.
Absence of Gdf11 does not rescue defects in Foxg1-/- cerebral cortex. (A) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of horizontal sections through the brains of wild type, Foxg1-/-, and Foxg1-/-;Gdf11-/- double mutants at E13.5. The cortex is severely reduced in Foxg1-/- embryos; absence of Gdf11 does not rescue this phenotype. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Expression of Foxg1 and Gdf11 in coronal sections through developing mouse brain. Foxg1 is abundantly expressed in the telencephalon (except for the cortical hem) at E11.5 (expression boundary indicated by arrowheads). Gdf11 expression is apparent in the ventral telencephalon and OE at E11.5, but by E12.5 is restricted to ventral midline of the telencephalon and the nascent hippocampus (arrows). At E15.5, no Gdf11 expression is apparent in the rostral telencephalon, whereas Foxg1 levels are high, especially in dorsal areas. Scale bars: 400 μm. C, cortex; CB, cerebral cortex; CH, cortical hem; CP, cortical plate; Di, diencephalon; H, hippocampus; LV, lateral ventricle; OE, olfactory epithelium; S, striatum; POA, preoptic area; SVZ, subventricular zone.