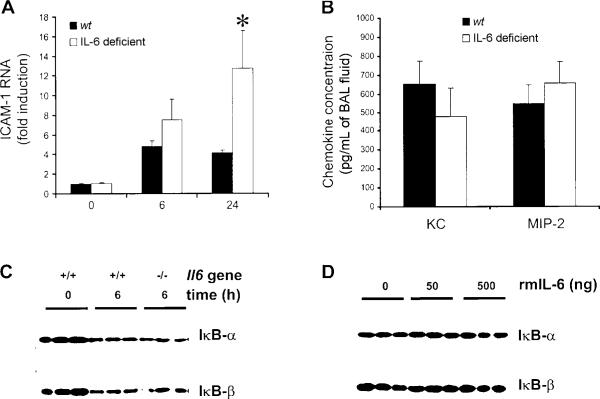
Figure 4.
Interleukin (IL)–6 and NF-κB–mediated gene expression during Escherichia coli pneumonia. A, Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)–1 RNA concentrations. Steady-state concentrations of ICAM-1 RNA did not differ between wild-type (wt) and IL-6–deficient mice. Lungs were collected from 10 mice/genotype at 6 h or from 3 mice/genotype at 0 and 24 h after infection. ICAM-1 transcripts were measured by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, normalized to 18s rRNA, and then expressed as the fold induction from 0-h levels, which did not differ between genotypes. Both time and genotype had significant effects (denoted by asterisk; P<.05 , 2-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni post hoc test). B, Concentrations of the NF-κB–dependent chemokines KC and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)–2. Chemokine concentrations did not differ between wt and IL-6–deficient mice (n = 5−6 mice/group). Lungs were collected 6 h after infection, and chemokine concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BAL) were determined using ELISA. There was no significant effect of genotype (Student's t test). C, Inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) content in the lungs. IκB content decreased during E. coli pneumonia but did not differ between genotypes. The IκB content was assessed by immunoblotting at the indicated time after infection. Each lane contains protein from an individual mouse that was either homozygous (+/+) or mutant (−/−) for the Il6 gene. D, IκB content in the lungs and IL-6. IκB content was not affected by the intratracheal instillation of recombinant murine (rm) IL-6. IκB content in wt mice that received the indicated dose of rmIL-6 was assessed by immunoblotting. Each lane contains protein from an individual mouse.