Figure 5.
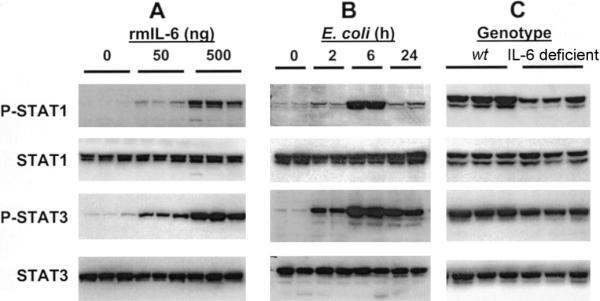
Interleukin (IL)–6 and activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins in the lungs during Escherichia coli pneumonia. Concentrations of tyrosine-phosphorylated (P) and total STAT proteins in the lungs were assessed by immunoblotting. Each lane contains protein from an individual mouse. A, IL-6 and phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 in the lungs. Recombinant murine (rm) IL-6 was instilled intratracheally to wild-type (wt) mice at the indicated dose per mouse, and lungs were collected 1 h later. The instillation of rmIL-6 was sufficient to induce phosphorylation. B, Phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 during E. coli pneumonia. Lungs were collected from wt mice at the indicated time after infection, and phosphorylation was assessed. C, IL-6 deficiency and STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation. Lungs were collected from wt and IL-6–deficient mice 6 h after infection, and phosphorylation was assessed. IL-6 deficiency decreased phosphorylation.
