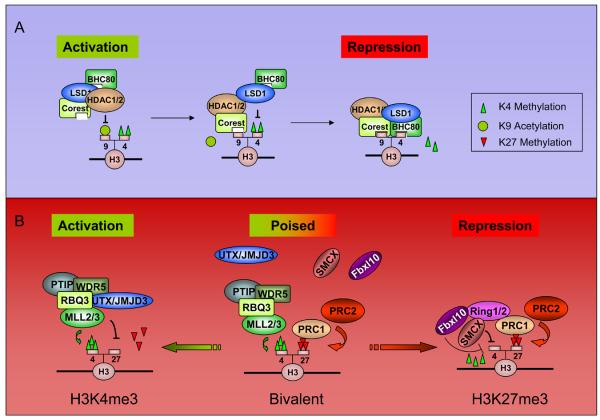
Figure 2. Diagrams of possible epigenetic mechanisms that involved in H3K4me and H3K27me regulation.
A) KDM1/LSD1-mediated H3K4me2 demethylation. A stepwise working model for KDM1/LSD1 complex is illustrated. The whole process involves HDAC-mediated deacetylation, CoREST binding, KDM1/LSD1-mediated H3K4 demethylation and BHC80 binding (H3K4me0). B) A proposed model for resolving bivalent domain to monovalent domain. In the pluripotency stage, the “bivalent domain” is established by MLL and PRC complexes, and the recruitments of H3K27 and H3K4 demethylases are absent. During differentiation, the methylase complexes are selectively kept and demethylases are differentially recruited, resulting in a H3K4me3-only or H3K27me3-only domain.