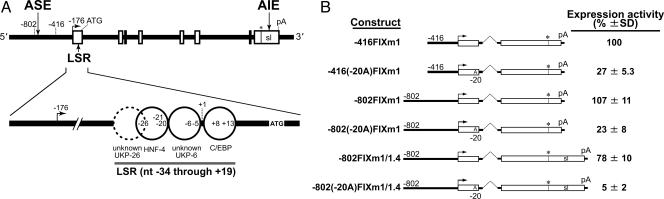
Fig. 1.
The hFIX gene and its minigene constructs with transient expression activities. (A) A schematic drawing of the hFIX gene and LSR. The hFIX gene is shown at the top with its 5′ end at left. Exons are shown by rectangles. Relative positions of ASE in the 5′ upstream, AIE in the 3′ UTR, and LSR in the 5′ UTR are shown. Right-angled arrow, asterisk with vertical thin line, and pA indicate the transcription start site, translation stop site, and polyadenylation site, respectively. The symbol sl (potential stem loop forming structure) in the last exon rectangle represents AIE. Solid line circles represent proteins binding to the wild-type LSR sequence while the dotted circle indicates the binding of UKP-26. Locations of representative mutations are shown with nucleotide (nt) numbering (12). (B) Human FIX minigene constructs and transient expression activities in vitro. Human FIX minigenes containing a representative Leyden phenotype mutation T-20A and their normal counterparts relevant to the present study are shown. These constructs extend 5′ end to nt -802 or nt -416, and have the middle portion of the 3′ UTR deleted (m1) or not deleted (m1/1.4). Transient expression activity levels relative to that of -416FIXm1 (approximately 50 ng/106 HepG2 cells/48 h) are shown at the right with SDs (averages of 5 independent assays).