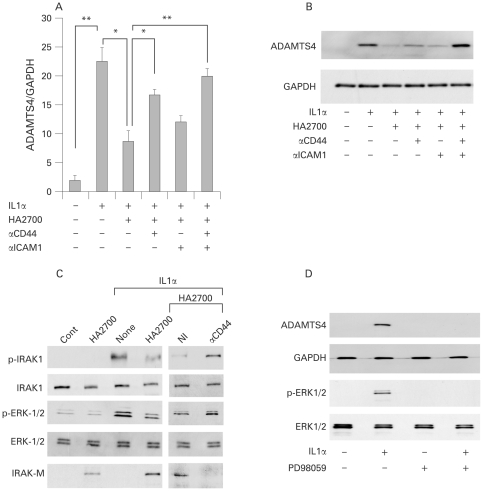
Figure 4.
Analysis of the involvement of the CD44 and intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1) signalling pathways in the HA2700 inhibitory effect on ADAMTS4 expression. (A,B) Effect of CD44 antibody (αCD44) and ICAM1 antibody (αICAM1) on the inhibition of ADAMTS4 expression with HA2700. Osteoarthritic chondrocytes were allowed to react for 1 h with buffer alone, non-immune IgG (20 μg/ml; data not shown), αCD44 (20 μg/ml), αICAM1 (20 μg/ml) or αCD44 (20 μg/ml) + αICAM1 (20 μg/ml), treated with 2.5 mg/ml HA2700 for 24 h, and then cultured for 24 h for the real-time PCR analysis of ADAMTS4 gene expression (A) and for 48 h for immunoblotting analysis of ADAMTS4 protein (B) after the addition of IL1α (1 ng/ml) to the culture medium. Bars are mean (SD) (n = 3). *p<0.05; **p<0.01. (C) Analysis of signalling pathways of IL1 and CD44 under treatment with HA2700. Expression of IL1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK1), extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase1/2 (ERK1/2) and IRAK-M and phosphorylation of IRAK1 and ERK1/2 were examined by immunoblotting of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. The cells were cultured for 24 h in the absence (Cont and None) or presence (2.5 mg/ml) of HA2700, and then stimulated for 30 min without or with IL1α (1 ng/ml), followed by immunoblotting for p-IRAK1, IRAK1, p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2 and IRAK-M. The effect of αCD44 on HA2700-induced signalling was examined as described above. (D) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) in ADAMTS4 expression and phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Chondrocytes were treated for 30 min without or with PD98059 (50 μM). Then, the cells were cultured in the absence or presence of IL1α (1 ng/ml) for 48 h for immunoblotting of ADAMTS4 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) or for 30 min for immunoblotting of p-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2. All experiments were performed in triplicate.