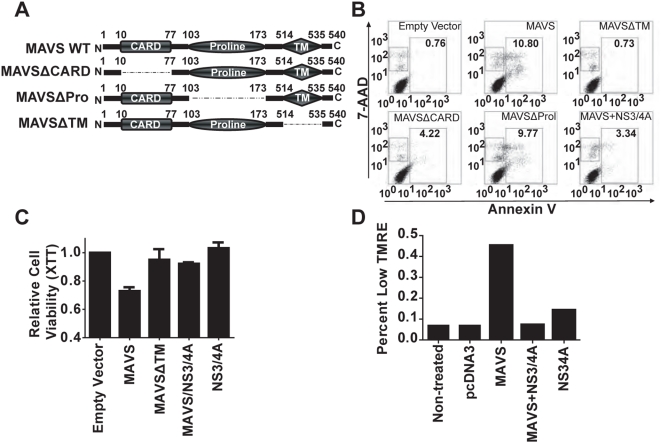
Figure 4. Distinct MAVS domains are required for apoptosis.
(A) The domain structure of MAVS. MAVS contains a N-terminal CARD-like domain, a C-terminal transmembrane domain (TM) and a central proline-rich region. The cartoon shows the structure of the three truncation mutants we used in the study. (B) The TM and CARD-like domains are not dispensable for the pro-apoptotic function of MAVS. 1 µg of wildtype MAVS and its three mutants depicted in (A) were introduced in HEK293T cells; and apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry 48 h post-transfection using 7-AAD and Annexin V as markers of dead and apoptotic cells respectively. (C) The mitochondrial localization of MAVS is critical for its pro-apoptotic function. Cell viability was determined by XTT assay. (D) MAVS induces mitochondrial membrane potential collapse in HEK293T cells as quantified by TMRE staining. Each graph represents two separate experiments.