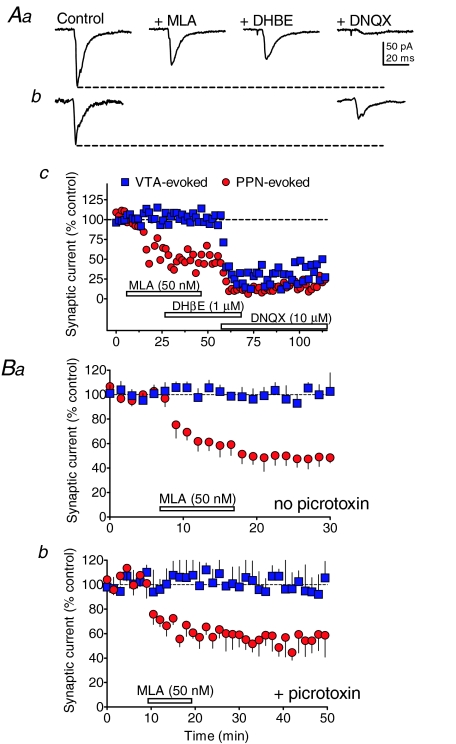
Figure 6. Effects of nAChR antagonists on PPN- and intra-VTA-evoked synaptic currents in VTA neurons.
Aa, PPN-evoked synaptic currents collected during the indicated pharmacological treatment from the same neuron represented in c. b, intra-VTA-evoked synaptic currents collected during the indicated pharmacological treatment (labels in a) in the same neuron as shown in c. c, time course of drug effects (indicated by the horizontal bars) on PPN- (red circles) and intra-VTA-evoked (blue squares) synaptic currents in the same VTA neuron. Note that the α7-nAChR antagonist MLA reduced the PPN-evoked response, but did not affect the VTA-evoked response. DHβE did not affect either synaptic response, and DNQX reduced both the PPN- and VTA-evoked responses in this cell. B, mean time courses of the effect of the α7-nAChR antagonist on PPN- and VTA-evoked and synaptic currents in the absence (a) and presence (b) of the GABAA blocker picrotoxin (100 μm). Note that MLA had no effect on the VTA-evoked responses, and that its inhibitory effect on PPN-evoked currents was unaffected by picrotoxin. This indicates that the effects of MLA were likely on glutamate, and not GABA release during PPN stimulation.