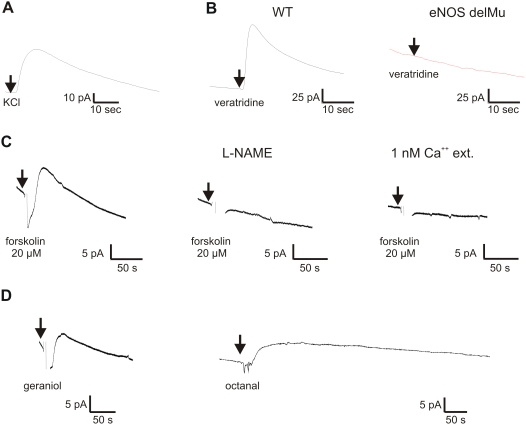
Figure 3. Amperometric NO-recordings of individual OSNs of wild-type, OMP-GFP, or eNOS-deficient mutant mice.
A, Application of KCl (45 mM) induces a robust NO-signal in an isolated wild-type OSNs. B, Veratridine (10 µM) induces a NO-signal in a wild-type OSN, but fails to induce NO release in an OSN of an eNOS-deficient mutant mouse (eNOS-delMu). C, Stimulation of the olfactory signal transduction pathway with forskolin (20 µM) led to a clear NO-signal in OSNs of OMP-GFP mice. Signals could be prevented by pre-incubation with L-NAME (1 mM) or by performing the experiments in extracellular medium with low Ca2+-concentration (1 nM). D, Application of the odorants geraniol (200 µM) or octanal (500 µM) produced NO-signals in OMP-GFP mice. Arrows mark the application of the indicated stimulus. Large deflections of the signal at the time of application represented artefacts that occurred in some experiments (forskolin, geraniol). These artefacts were blanked for clarity.