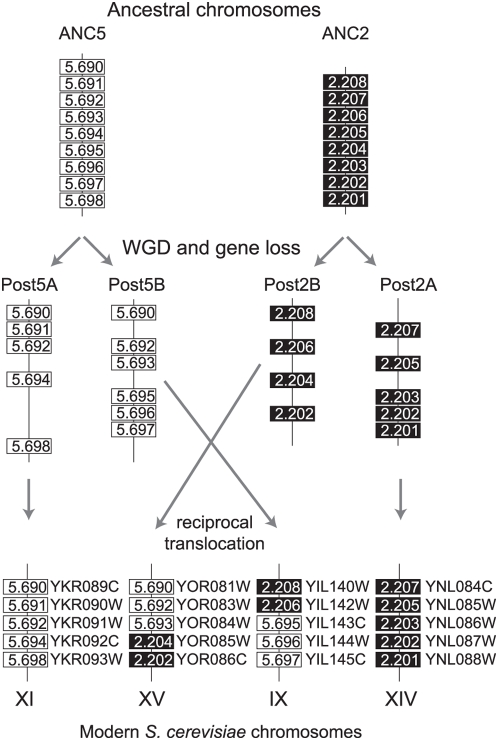
Figure 3. Example of a simple reciprocal translocation in S. cerevisiae.
Parts of two ancestral chromosomes, ANC5 and ANC2, are shown at the top. After WGD, these formed four chromosomes (labeled Post5A, Post5B, Post2A, Post2B), each of which retains a subset of the ancestral gene sets. Parts of S. cerevisiae chromosomes XI and XIV are derived from chromosomes Post5A and Post2A, respectively, without further rearrangement. A reciprocal translocation between chromosomes Post5B and Post2B gave rise to part of S. cerevisiae chromosomes XV and IX.