Figure 1.
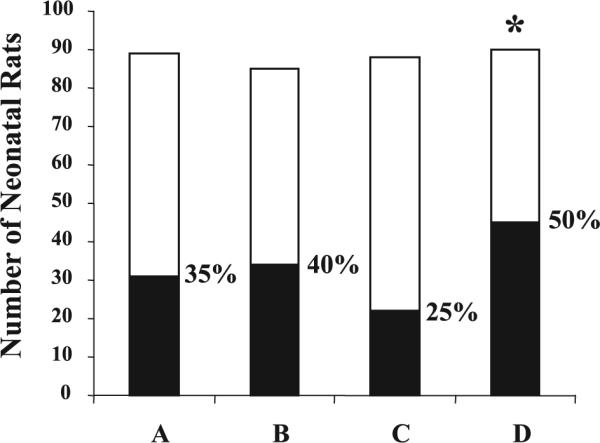
PUFA reduced the incidence of NEC in neonatal rats (p < 0.05). Neonatal rats were randomly assigned to four different supplementation groups: A (AA+DHA, n = 89); B (egg phospholipid, n = 85); C (DHA only, n = 88); and D (control formula, n = 90). Number (n) represents the total neonates in each group. Control formula-fed neonates had significantly higher incidence of NEC than all PUFA-supplemented groups (p < 0.01). □: NEC (−);■: NEC (+).
