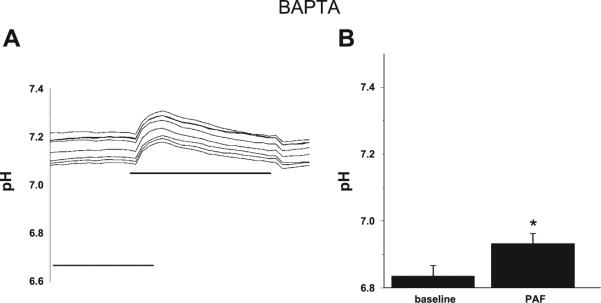
Fig. 3.
PAF-induced intracellular acidification of IEC is inhibited by Ca2+ chelation. A: representative tracing of pH measurements in IEC-6 cells by microfluorimetry using the pH-sensitive fluorescence dye SNARF. Cells were loaded with BAPTA 5 μM before treatment with PAF 3 μM. In contrast to control cells (Fig. 1), no acidosis is seen in n > 3 separate experiments, each representing minimum 7 cells/experiment all with similar results. B: summary data from separate experiments with measurements taken from >7 cells/experiment indicating no PAF-induced acidosis in the presence of BAPTA. Asterisk indicates statistical significance at P < 0.05 compared with baseline conditions.