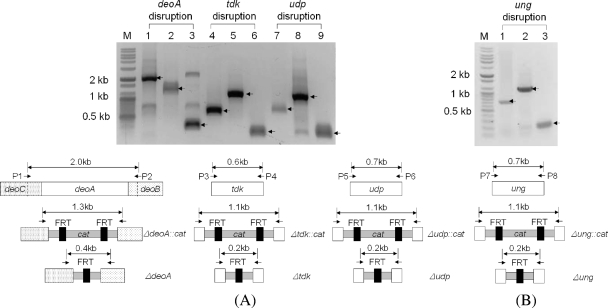
FIG. 3.
PCR analysis of three disruption mutants. P1 to P8 refer to priming sites. PCR amplification for identifying the deletion of each target gene was performed using each E. coli BL21 mutant genomic DNA as a template. (A) Salvage pathway gene disruptions. M, size marker; lane 1, deoC and deoB region including deoA (2.0 kb); lane 2, ΔdeoC::cat::ΔdeoB (1.3 kb); lane 3, Δ(deoC-deoB) (0.4 kb), represented to ΔdeoA; lane 4, tdk (0.6 kb); lane 5, Δtdk::cat (1.1 kb); lane 6, Δtdk (0.2 kb); lane 7, udp (0.7 kb); lane 8, Δudp::cat (1.1 kb); lane 9, Δudp (0.2 kb). The FRT (black bar)-flanked chloramphenicol-resistant gene was amplified by PCR. The linear disruption PCR fragment (gray bar) was transformed into a strain expressing the λ Red recombinase, and then chloramphenicol-resistant transformants were selected. The selective marker was eliminated by FLP recombinase system. (B) ung disruption. Lane 1, ung (0.7 kb); lane 2, Δung::cat (1.1 kb); lane 3, Δung (0.2 kb).